The Reasons for Low or No Engine Compression
There are plenty of reasons behind low engine compression. A car engine consists of plenty of small parts. Like any mechanical part, they experience mechanical failure at some point, and a few of them are directly related to the compression loss.
Let’s find out the possible causes for an engine to lose compression in the cylinders.
The Reasons for Low or No Engine Compression
Some components including valves, pistons, and piston rings are responsible for reducing the compression in the cylinders. When these parts are damaged or have any leak, the engine will struggle and may not even start at all.
We’re going to discuss the causes for low or no compression in one and all cylinders.
Low Compression In One Cylinder
Some internal engine damage is the reason for the engine to have low compression in one cylinder. It could be a piston with a hole or a broken connecting rod, a bent push rod, a valve with a broken spring, or a damaged or leaked valve. A worn-out camshaft will also create this problem.
Low Compression In All Cylinders
When you experience low engine compression in all cylinders, it indicates that the engine has excessive fuel that washes the cylinders. That flooded oil acts as sealing between several parts including the piston, cylinder walls, and ring assemblies.
SEE MORE
- The Truth behind the Higher Compression Ratio of Diesel Engines
- The Ultimate Guide to Fixing Low Compression in One Cylinder
No Compression In One Cylinder
In case of absolutely zero compression in one cylinder, check these following components to find out the problem.
First, examine the valve seat. A crack there will leak hot gases, burning both the valve and the seat. This cracking results from variation in the metal expansion rate. Cylinder heads are aluminum but the valve seat is made of a different metal. They expand at different rates under heat and pressure. This variation causes the seat’s displacement from the cylinder head, causing the cylinder to lose compression.
A broken seal in the valve head will cause damage to the cylinder head and the piston along with making a way for compression to leak. Similarly, some metal pieces keep the valve in place. The cylinder will lose compression if any of these pieces is dislodged. A broken valve spring will also create the same problem as this spring’s function is to keep the exhaust and intake valves closed.
A piston is made of aluminum. But it can also suffer damage under excessive heat or pressure. It could melt, get burned, or have a hole in it, causing the cylinder to lose compression to the point of null.
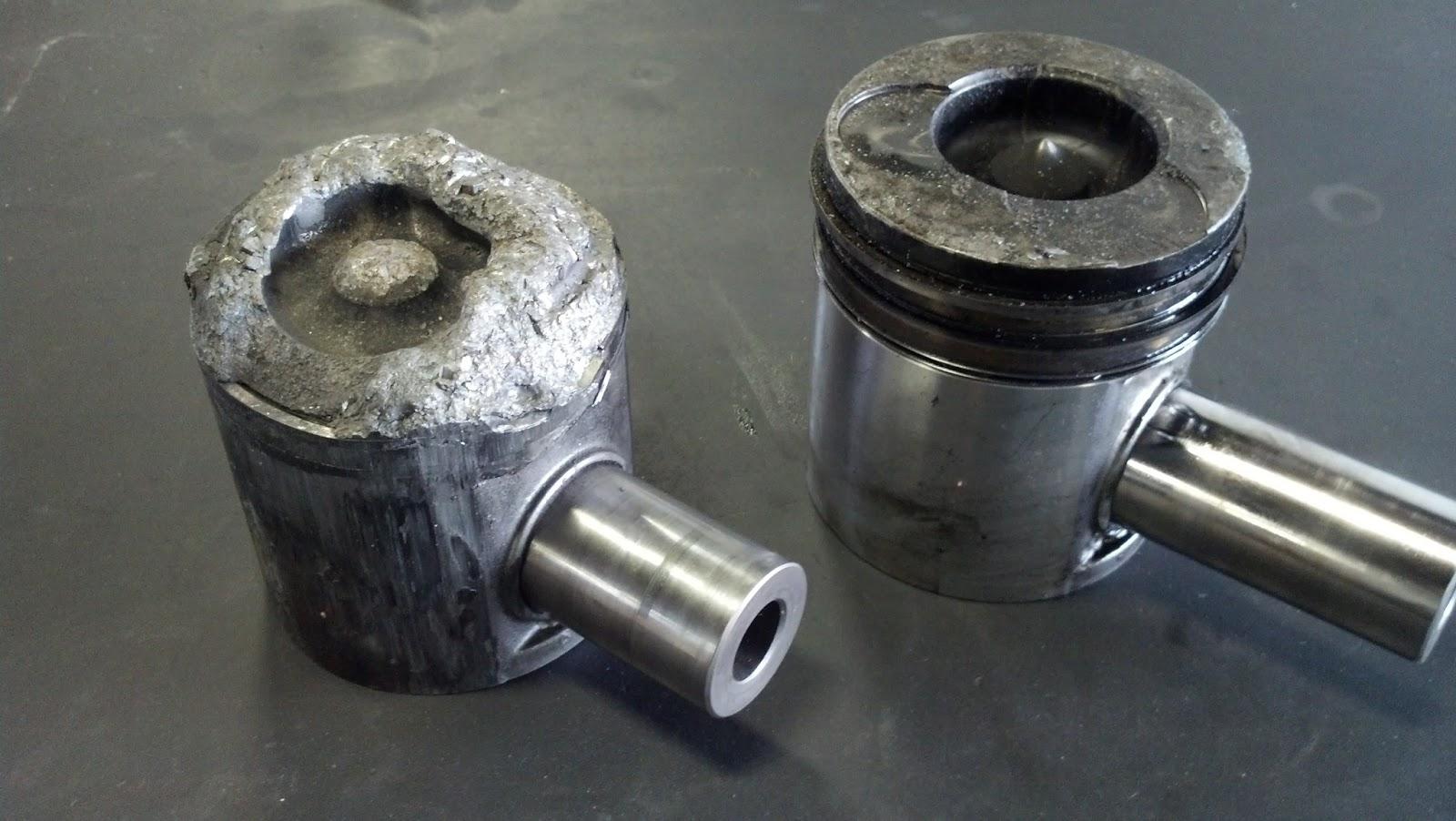

No Compression In All Cylinders
What could be the causes when there is no engine compression in any of the cylinders? Well, it’s either a broken timing belt or camshaft.
A timing belt keeps the camshaft linked to the crankshaft. But the camshaft cannot rotate when the belt fails, leading to the engine being unable to make compression. A broken camshaft will also create the same problem since its function is to open and close the exhaust and intake valves, and the engine will have no compression without these valves working properly.