Do Electric Cars Have Radiators
Electric vehicles (EVs) have become a prominent force in the automotive landscape. These silent powerhouses offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional gasoline cars. One key difference between these two technologies lies in their cooling systems.
Since electric cars lack internal combustion engines, a major source of heat in gasoline vehicles, the question arises: Do electric cars have radiators?
So buckle up and discover the secrets behind keeping these electric wonders cool!
Traditional Cooling Systems and Radiators
Internal combustion engines, the workhorses of traditional gasoline-powered cars, are like tireless athletes – they generate a tremendous amount of heat during operation.
This heat is a byproduct of the combustion process, where gasoline and air are ignited within the engine cylinders, propelling the car forward.
However, excessive heat can be detrimental to the engine’s performance and lifespan. Imagine running a marathon without ever cooling down – that’s what an engine would experience without a proper cooling system.
This is where the radiator comes in – it acts as the hero of the story, ensuring the engine stays within its optimal temperature range. The radiator is essentially a heat exchanger, located at the front of the car.
It consists of a network of thin metal fins and tubes filled with coolant, a special liquid that absorbs heat. As hot coolant circulates through the engine block, it absorbs the engine’s heat.
The coolant then travels through the radiator’s tubes, where air flowing through the car’s front grille helps to dissipate the heat into the surrounding environment. A fan mounted behind the radiator helps to draw air through the system more efficiently, especially when the car is idling or moving slowly.
Traditional cooling systems, while effective, do have some limitations. They can add complexity to the engine design and require regular maintenance, such as checking and replacing coolant. Additionally, leaks in the coolant system can lead to overheating, potentially causing serious engine damage.
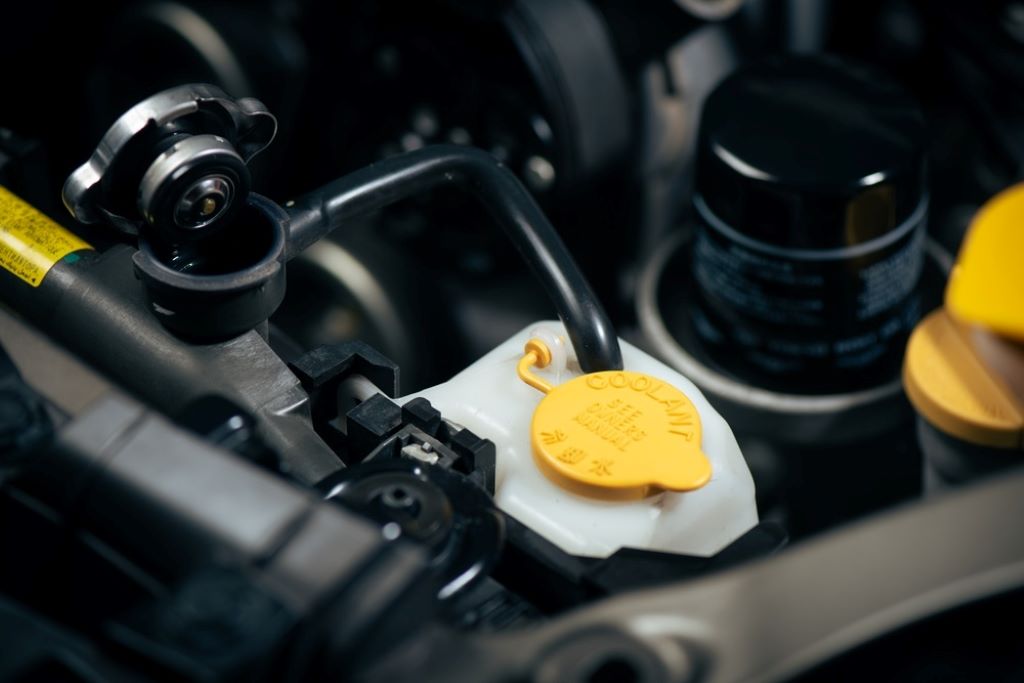

Do Electric Cars Have Radiators?
The fundamental difference between electric and gasoline-powered vehicles lies in their source of power. Gasoline engines rely on a process called internal combustion, where fuel and air are ignited within cylinders. This combustion process generates a tremendous amount of heat as a byproduct.
The engine must then expend additional energy to manage this heat, often requiring a complex cooling system with a radiator to prevent overheating.
Electric vehicles, on the other hand, operate on a completely different principle. They utilize electric motors powered by high-voltage batteries. Electric motors function by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to rotate the wheels.
While some heat is inevitably generated during this process, the amount is significantly lower compared to the intense heat produced by combustion engines. The lessened heat eliminates the need for a bulky radiator system like the ones found in traditional gasoline cars.
However, electric vehicles still require some form of thermal management to ensure optimal performance and battery health.
While they don’t need the robust cooling systems of gasoline cars, electric vehicles often employ alternative methods like liquid cooling or air cooling to maintain proper battery temperature.
Alternative Cooling Solutions for Electric Cars: Keeping Things Cool
While electric vehicles (EVs) eliminate the need for a traditional radiator, thermal management remains crucial for optimal performance and battery health.
Unlike gasoline engines that generate immense heat during combustion, electric motors operate much cooler. However, electric vehicles still require effective cooling systems for several key components.
Battery Thermal Management
The battery pack is the heart of an electric car, and maintaining its optimal temperature range is critical. Two primary methods are employed for battery cooling.
- Liquid Cooling: This is the more common and efficient approach. A network of coolant channels runs throughout the battery pack.
A pump circulates a coolant liquid, which absorbs heat from the battery cells and transfers it to a radiator located at the front of the vehicle. Air flowing through the radiator then helps dissipate the heat.
- Air Cooling: This method is typically used in smaller EVs or those with less powerful batteries. Fans strategically placed around the battery pack circulate air to cool the battery cells.
While simpler and lighter, air cooling is less efficient than liquid cooling and might struggle to maintain optimal battery temperature in hot climates or during periods of high demand.
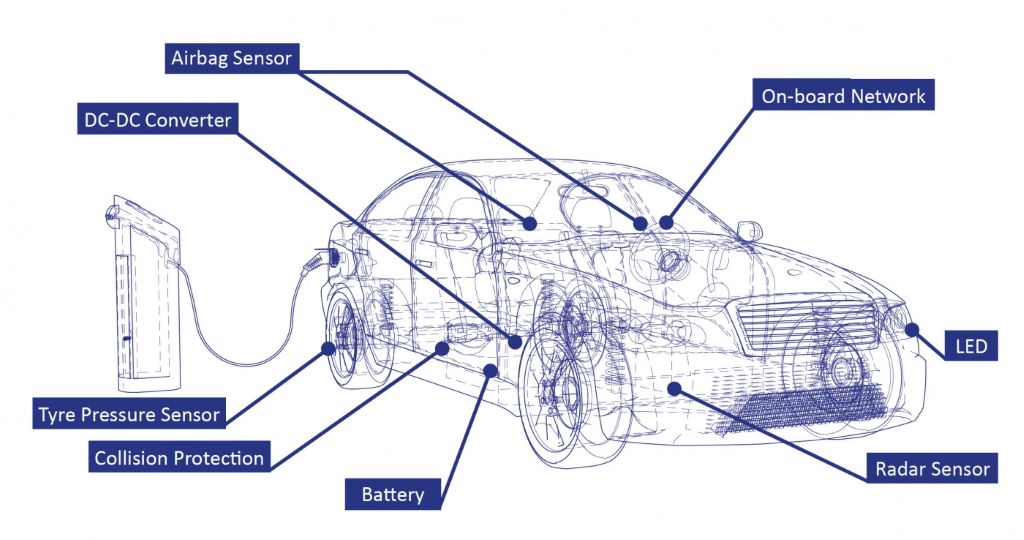
Additional Cooling Needs
Beyond the battery pack, other components in an electric car can also generate heat and require cooling.
Power Electronics
The power electronics module, which converts electricity from the battery pack to a form usable by the electric motor, can also generate significant heat.
Often, these modules are cooled using a separate liquid cooling loop or strategically placed heat sinks that dissipate heat into the surrounding air.
Electric Motor
While electric motors generate less heat than gasoline engines, they still require some level of cooling, especially under heavy load or during high-speed driving. Some electric motors employ a jacket filled with coolant that circulates around the motor housing to regulate temperature.
By implementing these alternative cooling solutions, electric car manufacturers ensure that all vital components operate within their optimal temperature range.
This not only optimizes performance and efficiency but also extends the lifespan of the battery pack, a critical element in any electric vehicle.

FAQs
-
Do electric cars use the same type of radiators as traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles?
Electric cars do not use the same type of radiators as ICE vehicles. While they do have cooling systems, these are typically designed to manage the heat generated by the battery pack, electric motor, and power electronics, rather than the engine cooling found in ICE vehicles
-
How does the radiator system in an electric car differ from that in a gasoline or diesel car?
In an electric car, the radiator system is often more compact and is focused on cooling the battery, motor, and inverter.
These components generate heat during operation, but the overall thermal management requirements are different and often less intensive compared to the cooling needs of a combustion engine.
-
Can the cooling system in electric cars impact their performance and range?
The cooling system can significantly impact an electric car’s performance and range. Efficient thermal management ensures that the battery and motor operate within optimal temperature ranges, preventing overheating and maintaining efficiency, which in turn can extend the vehicle’s range.
-
Do electric cars have multiple cooling circuits or just one?
Many electric cars have multiple cooling circuits to handle the different thermal management needs of various components.
For example, there might be separate circuits for the battery pack, the electric motor, and the power electronics, each optimized for its specific cooling requirements.
-
What role does a heat pump play in the cooling system of an electric car?
Some electric cars use heat pumps as part of their thermal management system. A heat pump can move heat from the battery and other components to the cabin for heating, improving overall energy efficiency, especially in colder climates.
-
How does ambient temperature affect the cooling needs of an electric car?
Ambient temperature plays a significant role in the cooling needs of an electric car.
In hotter climates, the cooling system needs to work harder to maintain optimal temperatures for the battery and motor, while in colder climates, the system might need to balance cooling with heating to ensure components stay within their operational temperature range.
-
Are there any maintenance differences between the cooling systems of electric and traditional cars?
Maintenance for the cooling system in electric cars is generally less frequent and simpler compared to traditional cars, as there are fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes.
However, it’s still important to regularly check coolant levels and ensure that the thermal management system is functioning correctly.
-
Do electric cars use air cooling or liquid cooling for their components?
Electric cars can use either air cooling or liquid cooling, but liquid cooling is more common in modern electric vehicles due to its greater efficiency in managing heat for high-performance batteries and motors.
Check out this video from Engineering Explained to learn more why don’t electric cars have multiple-gear transmissions!
Final Words
As electric car technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in thermal management. Research into new cooling materials and more efficient air cooling systems holds promise for even better performance and range in future electric vehicles.
So, the answer is clear for the question “do electric cars have radiators” – electric cars don’t need traditional radiators. Instead, they rely on a new generation of cooling solutions, paving the way for a cleaner and cooler future for transportation.