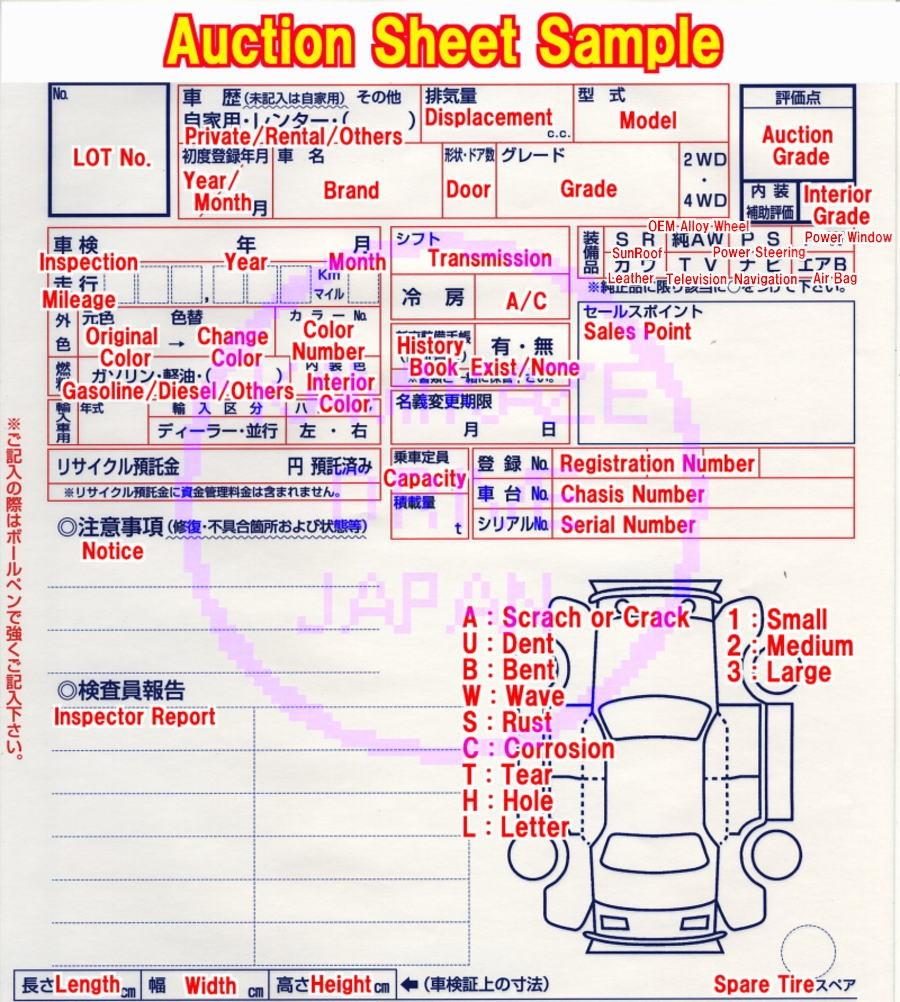
Air Bag Deployment: What Are The Required Conditions?
Airbag is by far one of the most important automotive security system. When an accident happens, the airbag will operate and reduce most of the damage for the driver and other people in the car. Yet many drivers do not know airbag deployment conditions nor its operation to deploy. In this article, we will tell you more about how air bag system works and in what exact conditions the airbag would deploy.
The Deployment Of Air Bag
The airbag control Unit (or ACU) is the main part that controls the airbag through impact calculation and chemical mixture. The rapid speed and safety of this technology turn airbags into the safest system for automobiles.
How does the airbag work?

Through many related sensors car parts like impact sensors, side pressure sensors, accelerometers, brake pressure sensors, wheel speed sensors, gyroscopes,…, the ACU can determine and be ready to trigger the bag when the crash occurs. In order to do that, an initiator or electric match is very essential.
ACU initiator takes the role of initiating the gas generator. An electrical conductor inside it is the key to this activity: When the conductor obtains enough heat, it ignites the combustible material wrapping around it and rapidly forces the gas to the airbag.
Once the required threshold has been reached, the ACU will immediately inflate the airbag by triggering the gas generator and letting the gas fill the space through vent holes.
Watch a video to understand more about the operation of the airbag:
The inflation only happens in approximately 60 milliseconds after the first contact. The airbags will protect both drivers and passengers from direct impact. After that, the gas will escape through these holes, which makes the airbag become smaller over time for the driver to get out. The ACU developers also have carefully calculated the inflation time. The airbag must inflate to its full state quickly enough to protect the drivers from the vehicle’s interior. If the time of deployment is too slow or too fast, passengers can be injured by contact with the interior or even the airbag itself.
What about the impact from the side you might ask? Thanks to various signals from car sensors, the ACU can calculate the force and the angle of the impact, as well as other variables, in order to perform seat belt pre-tensioners or airbag inflation. For that reason, according to airbag safety rules, drivers must wear seatbelts at all costs. Depending on these calculations, direct and side impact will never be a big trouble with the ACU.
Airbag deployment conditions

Many people are wondering: How can the airbag know exactly when to deploy? It needs a special airbag control part for this. The airbag system contains a sensor called MEMS accelerometer, a small circuit with integrated mechanical elements. These microscopic elements will capture and recognize sudden deceleration, and then send a signal to trigger the airbag. In the United States, the minimum speed for airbag deployment is 23 km/h (14 mph).
5 years ago till today, temperature has been the essential element in airbag deployment conditions. When the heat from the vehicle fire reaches 150 to 200 °C, the airbag will automatically deploy. This feature is not only safer for the drivers but also reduces the chance of causing explosions of the airbag.
Today, the condition to trigger the airbag is more complex. Since the real-life collisions are usually different than those in the lab, in order to boost the efficiency, the researchers must reduce inconsequential deployments, the occupant weight, seat belt, and driving seat location, as well as recalculate the speed to crash conditions.
Inflation
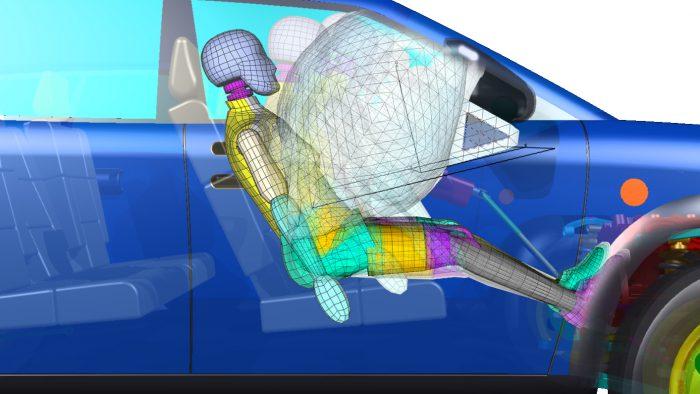
When it comes to opening the frontal airbags, it is the job of the inflator unit. Thanks to the signal sent from MEMS, an igniter starts a chemical reaction to generate nitrogen gas for airbag filling. The total process from deployment to inflation is approximately 0.04 seconds, which is rapid in order to reduce the risk of the occupant hitting car parts.
Some airbags use energetic propellants, while other technologies apply argon gas. The amount of propellants is different with each airbag, depending on the location on the automobile. The airbag in the passenger side container usually holds 200 grams of sodium azide, while the one on the driver side contains just 50 grams.
Read more:
- Perfect Guide To Be A Master In Automatic Car
- Drivers Must Know These Tips To Avoid Rollover Accident
After the deployment
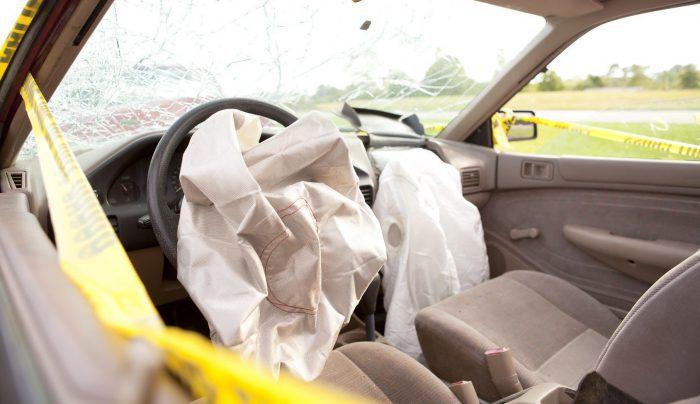

Once an airbag is triggered, the deflation will begin by releasing the gas through small vents in the cushion. Along with the gases, there is also the mixture consisting of French chalk, talcum powder, or cornstarch. This mixture will lubricate the airbag during the process.
In older designs, this dust contains azide-based propellant, which causes minor damage to soft body parts. However, after contact with air, the chemical mixture quickly becomes baking soda and creates almost no harm to car owners. Minor irritations only happen when the car windows are locked and closed completely for a period of time.
The Deployment of Airbag
Many people might be wondering: how fast does an airbag come out? Is it fast enough to save my life when I am traveling at a very high speed? In order to answer that question, drivers must find understand how the airbag works.
Crash sensors

This is, without a doubt, the most important part of the airbag system. In order for the airbag to know when to poop out, there must be car parts that can tell when the car is being damaged in an accident. How fast does an airbag come out will be decided by two factors, and the car sensor is one of them.
Crash sensors will respond to any sets of stimuli, relay the signals to the system, and orchestrate other safety features, from automatic door locks to airbag deployment. There are many different sensor types, which measure different things, from brake pressure, and brake impact, to wheel speed, seat occupant,… This is also the key to the airbag system and of course the most technologically advanced and expensive part.
Inflator
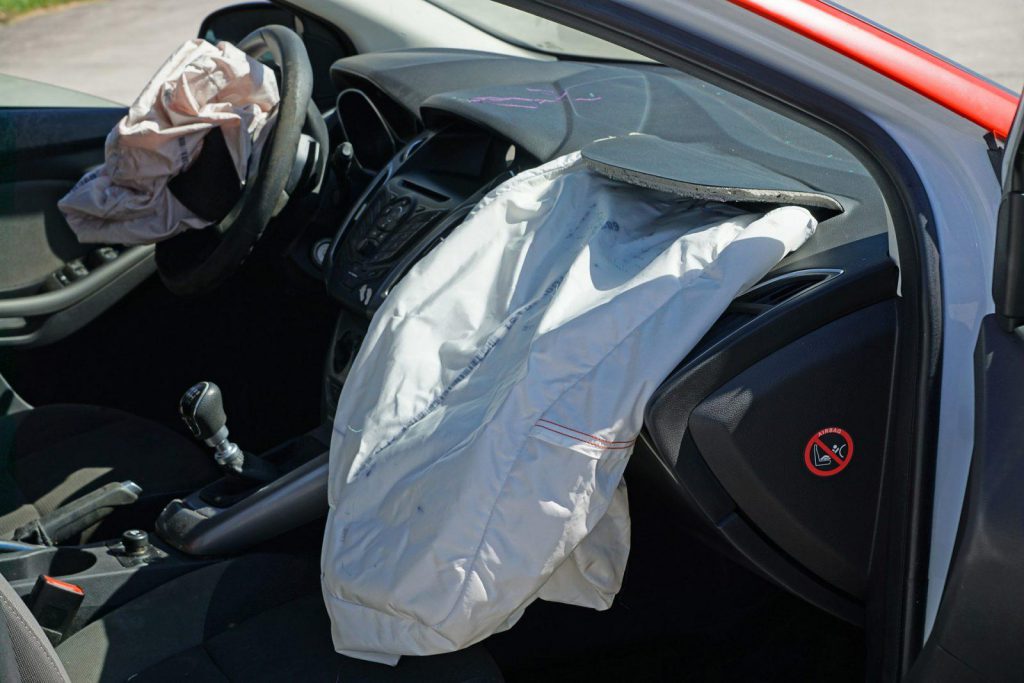

The inflator system is the place to receive the signal, which determines the question: how fast does an airbag come out? This part will set off a charge, which produces a nitrogen gas explosion and fills up the airbag. According to the study, this whole process only happens in 25 to 55 milliseconds. After that, the airbag will deflate itself through many small holes on the airbag’s surface.