Common Problems With LPG Converted Cars
The transition to Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) as a fuel alternative for vehicles is increasingly popular among drivers worldwide, driven by the desire to reduce fuel costs and minimize environmental impact.
LPG, a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, offers a cleaner, more cost-effective fuel option compared to traditional petrol or diesel.
However, while the benefits of LPG are compelling, converting a car to run on this alternative fuel comes with its own set of challenges and considerations.
What is LPG Conversion?
Liquefied Petroleum Gas conversion involves modifying a vehicle’s engine to allow it to run on LPG, in addition to or instead of its original fuel (usually petrol).
This process typically includes the installation of an LPG tank, fuel lines, injectors, and an evaporator, alongside the vehicle’s existing fuel system components.
Benefits of LPG Conversion
- Cost Savings: LPG is often cheaper than petrol or diesel, leading to significant savings on fuel costs over time.
- Environmental Benefits: Vehicles running on LPG emit fewer harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, contributing to cleaner air.
- Energy Security: Using LPG can reduce dependence on imported oil, contributing to energy security.
Drawbacks of LPG Conversion
Despite the benefits, vehicle owners considering LPG conversion should be aware of several potential challenges. The initial cost of conversion can be high, requiring upfront investment.
Not all vehicles are suitable for conversion, and modifications may void manufacturer warranties. LPG fueling infrastructure may be less developed than for traditional fuels, posing challenges for refueling.
Market Trends and Adoption
The adoption of LPG as a vehicle fuel varies widely by region, influenced by factors such as government policies, fuel prices, and the availability of conversion services and refueling infrastructure.
In some countries, incentives or subsidies are offered to encourage drivers to switch to LPG, accelerating its adoption.
Environmental Considerations
While LPG is touted for its environmental benefits, it’s important to recognize that it is still a fossil fuel. The production, distribution, and combustion of LPG still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, albeit less than traditional fuels.
Thus, while LPG can be part of the transition towards cleaner energy, the ultimate goal remains the adoption of renewable energy sources.
Overall, LPG conversion presents an attractive option for many drivers, offering a blend of economic and environmental benefits.
However, the decision to convert should be made after carefully considering the potential drawbacks and challenges, including the suitability of the vehicle for conversion, the cost implications, and the availability of LPG fueling stations.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve, LPG remains a viable interim solution for reducing vehicular emissions and fuel costs, while the world gradually shifts towards more sustainable energy sources.

Common Problems With LPG Converted Cars
Delving deeper into the common problems with LPG converted cars, each issue can significantly affect the overall driving experience and vehicle maintenance. Here’s a more detailed exploration.
Starting Issues in Cold Weather
LPG’s difficulty in vaporizing at low temperatures is a notable challenge. When the temperature drops, LPG remains in a liquid state rather than vaporizing, which is necessary for combustion in the engine.
This issue can lead to hard starts on cold mornings or require multiple attempts to get the engine running.
Manufacturers and conversion specialists often address this problem by installing an auxiliary system that initially uses petrol to start the engine and then switches to LPG once the engine reaches a suitable operating temperature.
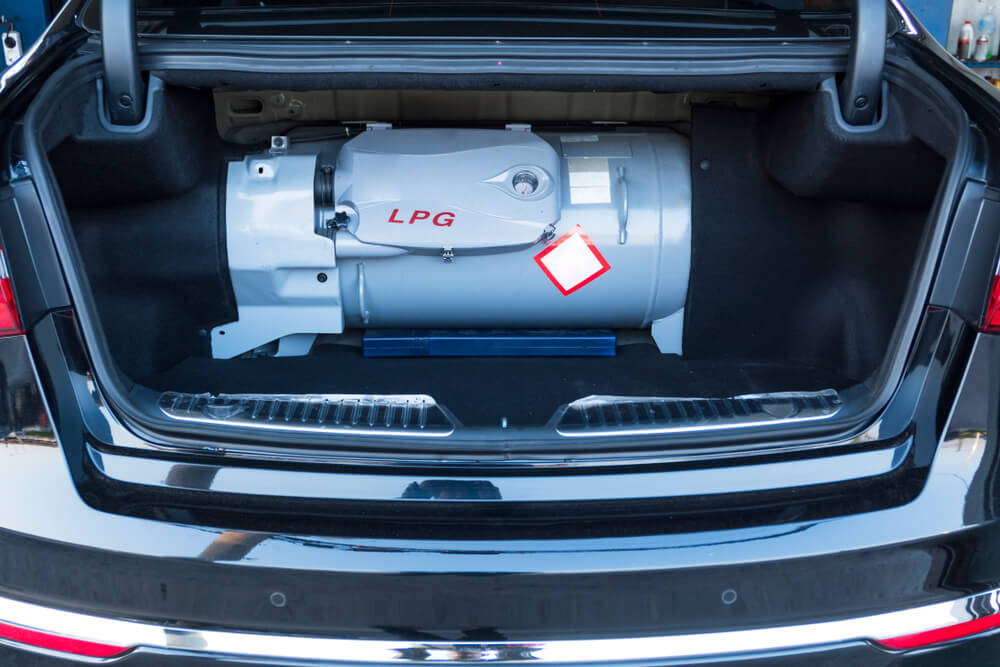
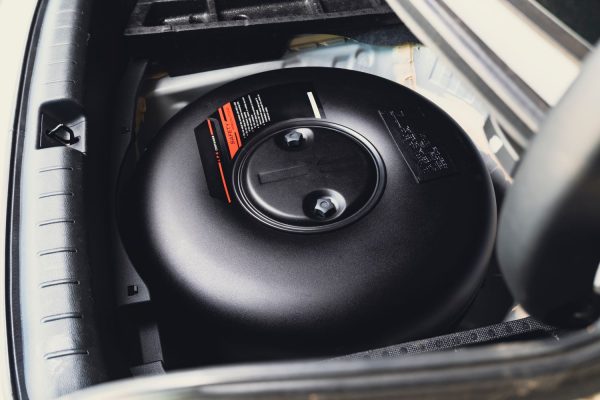
Reduced Boot Space
The space required for an LPG tank is a significant consideration, especially for smaller cars. LPG tanks are usually installed in the boot or, in some cases, where the spare tyre is housed, leading to a reduction in available cargo space.
This can affect the vehicle’s practicality, especially for families or individuals who require their vehicle for travel or carrying large items.
There are different types of tanks available (e.g., toroidal or cylindrical) that can minimize this impact, but the compromise on space is inevitable to some extent.
Increased Maintenance
Maintaining to make sure there will be no problems with LPG converted cars involves more than just the routine checks associated with petrol engines.
LPG components such as the vaporizer, which converts liquid LPG to gas, hoses, seals, and the tank itself need regular inspection for leaks or wear.
The system’s complexity means that specialized knowledge is often required for maintenance and repairs, which can lead to higher costs and the need for more frequent servicing compared to traditional fuel systems.
Valve Wear
The issue of valve wear is particularly prevalent in older engines that were not initially designed to run on LPG. LPG combustion creates higher combustion temperatures, which can accelerate the wear of engine valves and valve seats.
This can lead to decreased engine efficiency and performance over time. Some modern LPG conversion kits include hardened valve seats to mitigate this issue, but it remains a concern for many LPG vehicle owners.
Fuel Availability
The last culprit for our today’s problems with lpg converted cars is the availability of fuel. While LPG is widely used and available in many countries, the distribution of LPG fueling stations can be less dense compared to petrol and diesel stations.
This can pose a challenge for LPG vehicle owners, especially in rural or less populated areas. Planning is often required for long trips to ensure that refueling is possible along the route.
Despite these challenges, many users find the benefits of LPG, such as cost savings and reduced emissions, outweigh the inconveniences.

FAQs
1. LPG conversions affect engine performance?
While LPG is known for its cost-efficiency and lower emissions, some drivers notice a slight decrease in engine performance and power output after conversion.
This can be particularly evident in vehicles that haven’t been precisely tuned for LPG use, as the calorific value of LPG is different from that of petrol.
2. How does cold weather affect LPG conversions?
LPG-converted vehicles might experience starting difficulties in extremely cold weather. LPG’s vaporization rate decreases with temperature, which can lead to starting issues on cold mornings. Installing a quality vaporizer and ensuring proper maintenance can mitigate this problem.
3. Are there any specific maintenance requirements for LPG systems?
LPG-converted cars require specific maintenance to ensure the system functions correctly. This includes regular checks of the LPG tank, pipes, and connectors for leaks, as well as servicing the vaporizer and ensuring the fuel injectors are clean and functioning properly.
Neglecting these elements can lead to reduced efficiency or even system failure.
4. Can an LPG conversion void my vehicle’s warranty?
Converting a car to LPG can potentially void the manufacturer’s warranty, particularly if the conversion involves significant modifications to the engine or fuel system.
It’s essential to choose a certified LPG conversion specialist and discuss warranty implications beforehand. Some converters offer their warranties on the conversion to provide peace of mind.
5. How does LPG conversion impact insurance premiums?
Insurance premiums for LPG-converted cars can be higher than for their petrol counterparts. Insurers may view the LPG system as an additional risk factor or require a specialist policy.
However, informing your insurer about the conversion and ensuring the work is certified can help mitigate excessive premium increases.
6. Is there a risk of LPG tank explosions in accidents?
LPG tanks are designed to be highly robust and are subjected to rigorous safety tests, including pressure and crash resistance. The risk of an LPG tank exploding in an accident is very low, comparable to, or even less than, the risk associated with petrol tanks.
7. Can LPG conversions lead to fuel odor in the vehicle?
Improperly installed or maintained LPG systems can sometimes lead to a smell of gas in the vehicle, especially if there are leaks in the system’s components.
Understanding these common problems with lpg converted cars is crucial for current and prospective LPG vehicle owners.
It allows for informed decision-making regarding vehicle conversion and maintenance, ensuring that the benefits of LPG can be fully realized while minimizing its drawbacks.
Check out this video from Gadget John to get more information on the LPG cars after 2024!