What can prevent a car engine from starting? There are many reasons we can list out right now but among the causes, we can’t help but mention are car sensors.
But the problem is: there are thousands of sensors in your car, so what sensors can cause a car not to start? Let’s deep down into the article to find out the details!
Contents
- What Sensors Can Cause A Car Not To Start?
- How To Diagnose A Bad Sensor In Your Car?
- How To Fix Bad Sensors Causing Starting Issue In Cars?
- How To Prevent Bad Sensors From Causing A Car Not To Start?
- FAQs on Sensors Causing Car Not To Start
- Can a faulty ABS sensor actually stop my car from starting?
- Why does my car refuse to start after washing the engine bay, could it be a sensor issue?
- Why does my car refuse to start when parked on an incline, could it be a sensor issue?
- Why does my car only start when I wiggle the key in the ignition, could it be a sensor issue?
- Conclusion
What Sensors Can Cause A Car Not To Start?
As we know, automotive sensors collect and transfer input signals to the vehicle computer commonly called ECM (engine control module) so the ECM can process the signal to carry out its oppression correctly.
Technically, a sensor is a component that monitors the change in its environment and converts source information into an electrical signal that is sent to the control unit as input.
Sensors play a very important role in car operation. And there are plenty of them can cause a non-start situation!
Crankshaft position sensor
The first sensor you should check when your car doesn’t start is the crankshaft position sensor (CPS). This sensor is used to monitor the angle or the position of the crankshaft so that ECM can initiate the ignition firing for proper combustion.
With a bad crankshaft sensor, your car may not start at all. The crankshaft sensor is responsible for determining the RPM and position of the piston and then sends a signal to the ECM.
Combined with the signal from the camshaft, the controller can recognize the position of the piston and valve to adjust the timing of fuel injection and ignition for the appropriate cylinders.
So when the sensor fails completely, the ECM can’t read the exact data to initiate ignition firing and at that time your car won’t start or sometimes it starts and shut down immediately.

Camshaft position sensor
Among the sensors in the car, in addition to the crankshaft sensor, the camshaft position sensor (CPS) also plays a very important and indispensable role in the car. The purpose of this sensor is to measure the rotations and the position of the camshaft.
The ECM will use this data to know when to command the spark and fuel for the best engine efficiency. The camshaft and crankshaft position sensors often work in tandem to help the ECM calculate the optimal fuel injection and ignition timing for the engine.
So can a camshaft sensor cause a car not to start? The symptom you might be experiencing with a bad camshaft sensor is a delayed or no start since the ECM isn’t getting the correct data from the camshaft to start spark and fuel at the perfect time and it will stop your car from starting.
Read More: Camshaft vs Crankshaft: Working Methods Explained
Throttle position sensor
The throttle position sensor in the vehicle is used to find the exact position or angle of the throttle control valve inside the throttle body. This data is used to make arrangements on the fuel injection rates to get the optimum performance from the engine.
This sensor is also used by the traction control system to automatically adjust the throttle opening angle, compensate for the idle throttle or control the gearshift process (with automatic transmission vehicles) to provide stable operation.
When the TPS is bad, the computer may read a flat signal from the sensor. As soon as you put your foot on the accelerator, the throttle body opens up but the fuel injection rate will be lower as the sensor reads flat. This disturbs the fuel-air ration and your engine will stall or stop immediately.
Mass airflow
One of the sensors that make your vehicle not start is the mass air flow sensor. The MAF sensor calculates the amount of air entering the combustion chamber and transfers the data to the ECM.
The ECM will control to optimize the fuel ratio as well as adjust the ignition angle to improve operating performance and save fuel. Normally, the MAF sensor will be located on the air intake before the throttle.
The popular symptom to figure out when MAF sensors are bad is the car not starting. If the MAP sensor is giving a faulty reading of less air coming in, the ECM will command less fuel.
And at that time, your combustion chamber will don’t have enough fuel and air for the spark plugs to ignite and your automobile will be unable to start.
Related Post: What To Do After Replacing Mass Air Flow Sensor?
Fuel pressure sensor
If your car is having trouble starting or it’s not getting the power it needs, there’s a good chance that the fuel pressure sensor fails. Not every driver knows about what’s a fuel pressure sensor and its importance in-car operation.
A fuel pressure sensor is typically placed on top or inside of the gas tank. A fuel pressure sensor is a device that monitors the fuel pressure in the car’s fuel rail, it takes the information from the fuel rail and transfers this data to the ECM.
ECM will analyze the information and make adjustments to send the signal to the fuel pump control module to regulate the speed of the fuel.
Simply put, its primary function is to detect the pressure in the fuel system and enhance fuel economy. A certain amount of fuel is required to start your car and when your engine doesn’t get that amount of fuel, it won’t start.
The problem could be the result of the faulty fuel pressure sensor. The self-ignition process takes place due to the air mixture compression in the combustion chamber.
Regardless of the compression ignition engine or spark engine, without the incorrect amount of fuel, it can’t start.
Oil pressure sensor
Among the many sensors that cause your car to fail to start, the oil pressure sensor is one of them. It’s worth checking the oil pressure sensor when you notice that your car doesn’t start.
The oil pressure sensor is a simple electrical device that measures and controls the oil pressure and sends data to the electronic control panel.
Thanks to that, the driver easily knows the amount of oil being pumped into the system. If the oil is fully pumped, it will provide good lubrication, reduce friction, and help machines operate smoothly.
During the operation, this sensor monitors oil pressure and transmits the data to the ECM. Depending on the pressure level, the ECM will send a signal and adjust the right action for your car.
As an important part of the electronic control system, directly affecting the vehicle’s starting and accelerating process, the oil pressure sensor is required to work correctly.
If something goes wrong with this part, the ECM cannot send the correct signal to control the engine. The car not starting is an inevitable thing that will happen when the oil pressure sensor fails.
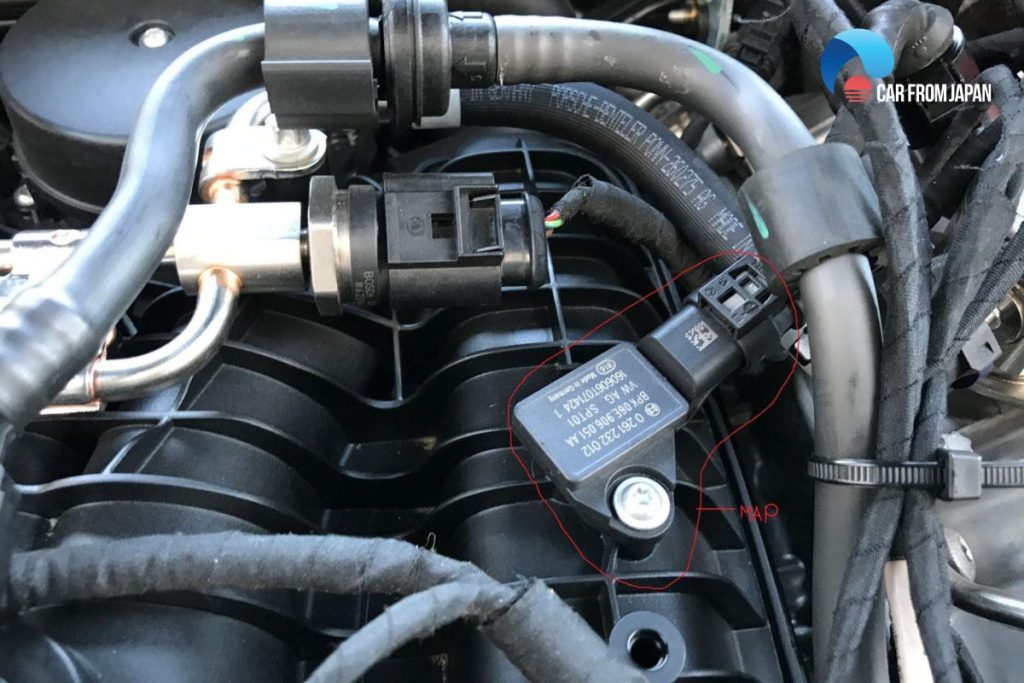
Manifold absolute pressure sensor (MAP)
The MAP sensor is attached directly to the intake manifold, or fixed in another location and connected to the intake manifold by a pipeline. The ECM relies on data from the MAP sensor to make calculations about the fuel injection and the ignition process.
MAP sensors in modern vehicles record the air pressure inside the inlet manifold to calculate the fuel injection and engine load parameters.
The MAP sensor is a very sensitive part to dirt. In particular, the intake pipe system is prone to clogging and leaking when cleaning is not careful, affecting the process of changing vacuum pressure.
Strong impacts during vehicle operation also have the risk of damaging the connections, causing damage to the sensor. So when the MAP sensor fails, your car acts lazy because the ECM will record the wrong data.
This can alter the fuel injection parameter and cause power loss. Because the MAP sensor should read the sudden vacuum created inside the manifold when cranking to initiate ignition parameters.
When this sensor can’t read the small changes inside the manifold, the car might find it hard or not to start at all. Sometimes the car might start after a few attempts or just pressing the accelerator slightly.

How To Diagnose A Bad Sensor In Your Car?
Suspect a faulty sensor is preventing your car from starting? To identify the culprit yourself, you need a few tips and tricks to find the right spot.
Here is a basic breakdown of how to diagnose sensors that may be malfunctioning when your car won’t start.
Check Engine Light (CEL)
Although it is a neglected component sometimes, the check engine light (CEL) can be a crucial diagnostic tool when trying to determine the cause of this problem.
Not all sensor failures trigger the CEL, but when it does, there can be a problem with the engine management system, such as a sensor malfunction.
If the CEL light is on, check it out with an OBD-II scanner. Plug it into the correct OBD-II port (usually under the dashboard) and retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes will often clearly identify the faulty sensor from the start.
Even if the code indirectly points to a sensor, it can still significantly narrow potential problem areas, making troubleshooting more efficient.
Visual inspection
In addition to machine diagnostics or more complex methods, a thorough visual inspection can also reveal why the car won’t start.
While looking, pay attention to the location of the sensors involved in the problem and check their wiring/connectors, such as the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, mass air flow sensor, or coolant sensor. Even a loose connection can disrupt the flow of information and prevent the engine from starting.
After checking around the sensor area, focus on the sensor itself for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or burns in the housing or connector.
Finally, a dirty sensor can also be the cause. One of the most common sensors to get dirty is the MAF mass air flow sensor. If it is not clean, carefully remove it according to the instructions and clean it with a specialized cleaner.
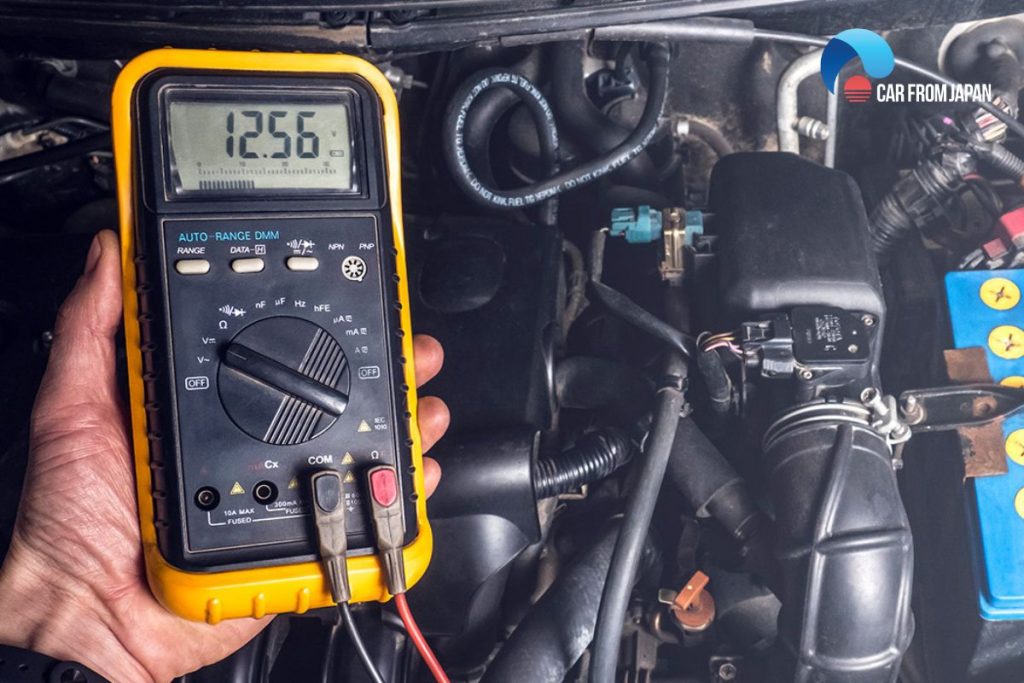
Use a multimeter
Another method for those familiar with electrical components is to use a multimeter to test the sensor.
Refer to the disassembly repair manual to understand the testing procedure, voltage/resistance readings, connection points, and safe-proper settings.
You can effectively test the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors with a multimeter. Determine whether the signal is transmitted correctly by measuring the voltage and resistance of the terminals. If the readings are abnormal, the sensor is faulty.
One thing to note is that you must disconnect the negative battery terminal before performing the sensor test to ensure safety.
Moreover, the throttle position sensor (TPS) can also be inspected this way. You can monitor the sensor’s output voltage when the throttle valve opens and closes.
Any spikes, dead spots, or inaccurate voltage readings indicate a faulty TPS, which can prevent starting or cause rough idling and poor acceleration.

Swap test
Another way to test a faulty sensor is to swap it out with a new spare sensor and try starting the car.
If it starts with the sensor installed, you have identified the faulty part. This method is helpful for crankshaft position sensors, MAF, or camshaft position sensors.
Mechanic inspection
Finally, if you lack the necessary tools and knowledge to test the sensor, taking the car to a mechanic is the most effective option. Although DIY repairs can save money, they can lead to further damage or even personal injury if not done properly.
Choose the most appropriate and effective option to save time, and effort to quickly identify the root cause of the problem.
How To Fix Bad Sensors Causing Starting Issue In Cars?
Here are some basic steps to take when dealing with faulty sensors. While some can be fixed with a simple cleaning, like the MAF sensor, others require a more involved procedure.
Gather the right parts
If a replacement is needed, make sure to buy the correct model and year of your vehicle. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reputable parts dealer.
Disconnect the battery
This is a critical safety step. Remember to disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the sensors to avoid electrocution and damage to the electrical system.
Locate the faulty sensor
Find the exact location of the sensor in your vehicle’s repair manual. The manual will also provide helpful instructions on how to access the sensor and any specific disassembly procedures.
Remove old sensor
Disconnect the electrical connector and remove the hardware securing the old sensor. Pay attention to the method of sensor installation and removal, as this will help you install the new sensor correctly.
Install the new sensor
When installing the new sensor, ensure it is properly seated and secured. Connect the electrical connector and any mounting hardware.
Double-check the newly installed connectors or wires for any loose connections or improper installation.
Reconnect the battery
Reconnect the vehicle’s negative battery terminal.
Clear Trouble Codes (if applicable)
If the Check Engine Light (CEL) is illuminated, use an OBD-II scanner to clear the stored trouble codes after installation. This will reset the system and prevent the CEL from turning on unnecessarily.

Check the vehicle
After completing all the standard operations and procedures according to the instructions, you can start the vehicle and check if it is operating normally. If the vehicle starts and runs smoothly, you have partially solved the problem.
Consult a specialist if necessary
If you have difficulty with the procedures or the vehicle does not start after replacing or cleaning the sensor, consult the experts at a reputable repair and maintenance facility.
How To Prevent Bad Sensors From Causing A Car Not To Start?
Regular maintenance tasks can help prevent no-start situations and sensor failures. Follow a routine vehicle inspection schedule that includes checking the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft position sensor, mass air flow sensor, and wiring and connectors.
This proactive approach can save you time/money and prevent long-term damage and frustration.
You should also maintain a clean engine compartment so that dirt or debris cannot contaminate and corrode the sensor heads and wiring inside.
However, when cleaning, avoid using high-pressure water jets, which can damage the sensors if you apply direct pressure.
When replacing sensors, prioritize choosing OEM parts or reputable and reliable aftermarket brands. Do not opt for cheap and unoriginal replacements as they can cause more serious consequences later.
FAQs on Sensors Causing Car Not To Start
Can a faulty ABS sensor actually stop my car from starting?
Surprisingly, yes! In modern cars with integrated safety systems, a failed ABS sensor can cause communication errors within the ECU, triggering a fail-safe mode that prevents the car from starting for security reasons.
Why does my car refuse to start after washing the engine bay, could it be a sensor issue?
Yes, water exposure can affect sensors like the crankshaft position sensor, camshaft sensor, or MAF sensor, causing them to short out or send incorrect signals.
This can result in an immediate no-start condition until they dry out.
Why does my car refuse to start when parked on an incline, could it be a sensor issue?
Yes, some vehicles have a fuel level sensor that inaccurately reads fuel levels when parked on an incline.
If the sensor falsely indicates an empty tank, the ECU may prevent ignition, assuming there’s no fuel available.
Why does my car only start when I wiggle the key in the ignition, could it be a sensor issue?
Yes, a worn-out ignition switch sensor or immobilizer sensor may have a weak connection, causing the vehicle’s security system to prevent starting.
Wiggling the key may temporarily restore contact.
Learning more about car sensors, grasp their basic specifications to identify its problems when issues happen!
Conclusion
Now you know what sensors can cause a car not to start. But please keep in mind, every car model will have different systems, so they will have different sensors that can cause a no-start situation.
Let’s make sure you diagnose the exact problem to have a suitable method for your car. If you have any concerns about this topic, don’t hesitate to leave your comment below.



Had my transmission changed left the macanic my truck died out saying low oil pressure and won’t start