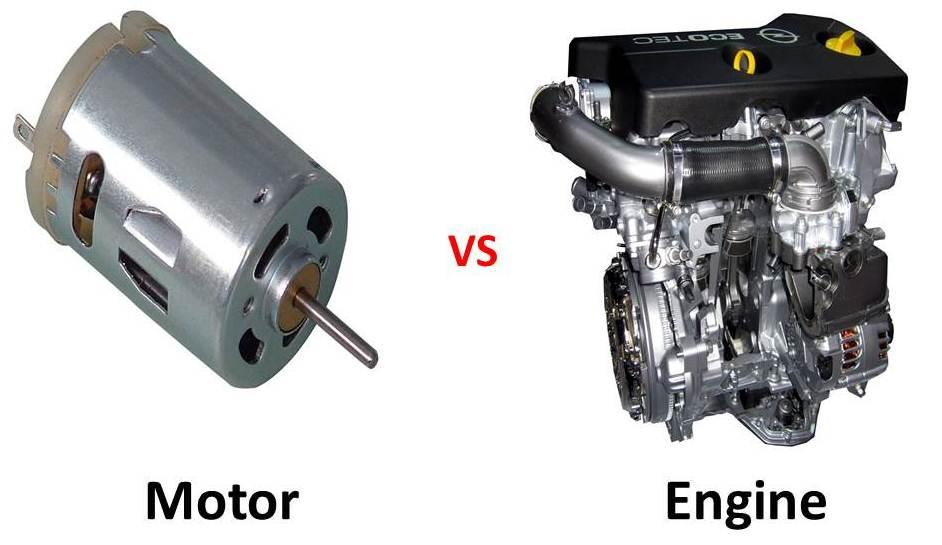
Could there be an argument about motor vs engine? It seems odd especially since we use these words interchangeably. However, these two words originally denoted very different things.
Contents
Motor vs Engine: The Definitions
The dictionary definition of ‘motor’ represents it as a machine that produces kinetic power as the primary output and sends it to an automobile or other devices.
On the other hand, an ‘engine’ is a complex machine with moving components that transform power into motion.

1. Motor
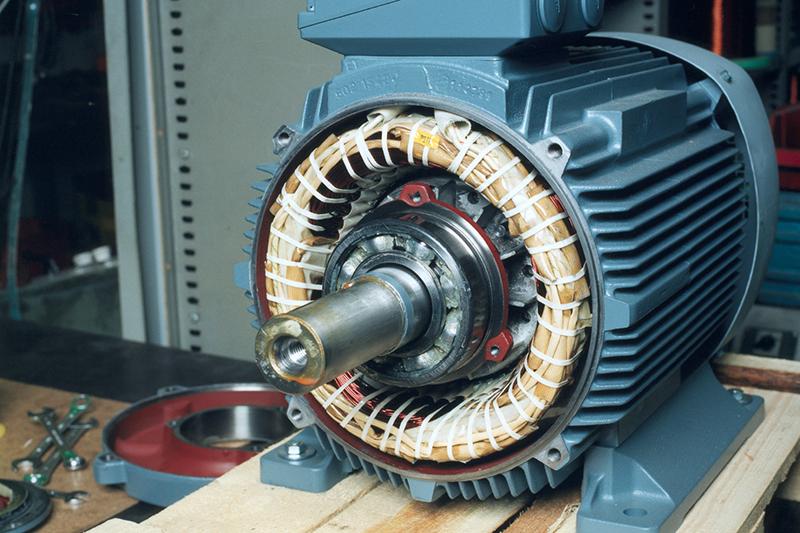
Most motors these days are electrical motors and they transform electrical power into mechanical energy. You can divide them into two broad categories – AC motor and DC motor.
AC current is the power behind running AC motors while DC electricity runs DC motors. You can divide these two types into more categories based on horsepower, power rating, and other factors.
2. Engine
The engine is a mechanical component that converts any form of energy into mechanical power. Based on the functions, you can put them into several groups.
For example, combustion engines transform heat into mechanical power while hydraulic engines produce mechanical energy from pressurized fluids. Similarly, the electrical engines convert electrical power.
If you take the engine of an automobile as an example, it converts the chemical power of fuel into heat through combustion, which means the transformation of heat into mechanical power.
On the other hand, a motor does nothing of this sort. It works as an actuator that converts electrical power or fluid energy to make a device work.
Motor vs Engine: The Components
The mechanisms of these two devices are quite different and they also have different types of components.
The engine has cylinders and pistons. The piston moves by the pressure created by the burnt fuel and pushes the cylinder to move.
A motor has a rotor and stator instead. The supplied electricity creates an electromotive force that makes the rotor move and generates mechanical power.
SEE MORE:
- Everything You Should Know about Types of Car Engines
- Facing the Engine Vibration Problem? Learn How to Fix It
Motor vs Engine: The Differences
As the definitions suggest, these are completely two different types of devices with separate functions. Follow the chart to know their differences:
| Engine | Motor |
| The word ‘engine’ usually refers to the reciprocating engine variations such as internal combustion or steam engines. | The word ‘motor’ is commonly used to indicate a rotating device such as an electric motor. |
| It produces mechanical power from chemical energy. | It transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy. |
| Most engines are run by fuel. | Motors mostly run on electricity or batteries. |
| Lubrication is needed for its components to run continuously with reduced friction. | No lubrication is needed. |
| Main components are pistons and cylinders. | Coils and rotors are the main components of motors. |
| Given that both devices produce the same power, an engine is heavier than a motor. | Motors are lighter than engines. |
| Engines are less efficient than motors because the ratio of fuel to converted energy is lower. | Motors are highly efficient because the percentage of lost power is minimal. |
| Engines are noisy. | Motors are relatively quieter. |
| Examples: Cars, trains, large ships, and more. | Examples: fans, washing machines, vacuum cleans, and more. |
FAQs
-
Can an internal combustion engine be called a motor?
Yes, an internal combustion engine can sometimes be referred to as a motor, but it’s more common to use the term “engine” for such devices.
Engines like those in cars, motorcycles, and lawnmowers use the combustion of fuel to generate mechanical power.
-
Are electric motors and electric engines the same thing?
Yes, in everyday language, the terms “electric motor” and “electric engine” are often used interchangeably. Both refer to devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, such as the motor in an electric vehicle.
-
Are there any exceptions to the motor vs. engine distinction?
While the distinction between motor and engine is generally as described, there can be regional or industry-specific variations in terminology.
Some areas or industries may use the terms differently or interchangeably, so it’s essential to consider the context.
-
What is the history behind the terms “motor” and “engine”?
The terms “motor” and “engine” have evolved over time. “Motor” originally referred to a source of motion or power, and “engine” referred to a mechanical device.
Over the years, “motor” became more associated with electric devices, while “engine” became associated with combustion-powered devices.
-
Are there any common examples of motors and engines?
Yes, common examples of motors include electric motors used in appliances, fans, and industrial machinery. Common examples of engines include gasoline engines in cars, diesel engines in trucks, and jet engines in airplanes.
-
Is there a fundamental difference in how motors and engines work?
Yes, there is a fundamental difference in how motors and engines operate.
Motors typically use electrical energy to generate mechanical motion through electromagnetic principles, while engines rely on combustion or other forms of energy conversion to produce mechanical motion.
Check out this video from Animagraffs to get an inside look at the basic systems that make up a standard car engine!
-
Can you provide some advantages of electric motors over internal combustion engines?
Electric motors often offer advantages such as higher efficiency, lower emissions, quieter operation, and the ability to use renewable energy sources. They are also more straightforward to maintain and can provide instant torque.
-
Why is it important to use the correct terminology when discussing motors and engines?
Using the correct terminology is important to avoid confusion and ensure effective communication, especially in technical and engineering contexts. Precise language helps convey the specific type of device or technology being discussed.
-
Are there any industries where the distinction between motor and engine is particularly significant?
The distinction between motor and engine can be crucial in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electrical engineering, where precise terminology is essential for clear communication and understanding of complex systems and technologies.
If you are still curious about the difference between, don’t hesitate to send your question to us in the box below, our auto experts will answer it for you.
Additionally, if you are interested in a Japanese used car with good engine, click here.