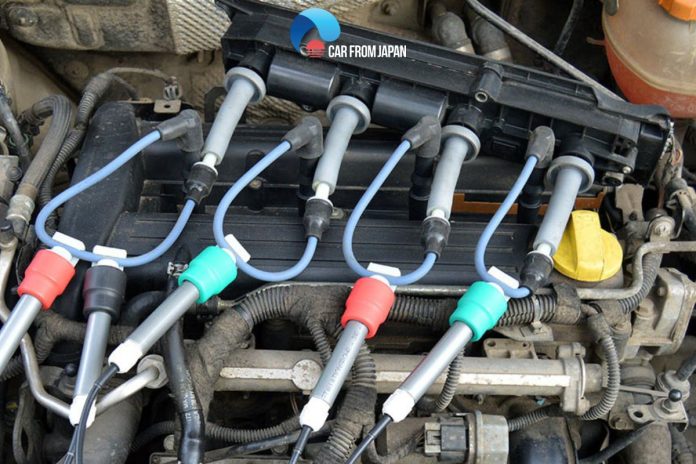
Have you ever wondered why old movies show mechanics working on a distributor cap, but you never see them on a modern car? The answer is a technology called the Distributorless Ignition System, or DIS. It’s a big improvement that changed how car engines create spark. That’s why in this article, we’re going to break down how the distributorless ignition system works and why it’s a major upgrade.
Contents
What Is a DIS Ignition System?
The DIS, also known as the Distributorless Ignition System, is the ignition system in which various induction coils replace the distributor of the electronic ignition system. The ICU, also known as the Ignition control unit, as well as the ECU (Engine control unit), will take care of the timing of the spark. This makes the whole DIS much more accurate as well as efficient.
With the introduction of the ignition system, this system became famous. In fact, there are various ignition systems created from these ideas. They are results of changes and improvements with the purpose of making the ignition system much more effective and reliable.
Why We Need the Distributorless Ignition System (DIS)
We come with the most famous 4: Magneto ignition system, glow plug ignition system, electric coil ignition system, as well as electronic ignition system. In this type, we will mainly focus on electronic ignition systems, as they are the technology used in most super and latest cars.
However, there are various reasons why we need the distributorless ignition system.
The reasons
Firstly, the electronic ignition system uses the distributor in order to distribute the voltage signal from the ignition module. And these high-voltage signals will come to the spark plugs. As we know, the distributor used is a mechanical part with a rotor that completes the circuit and controls the spark timing. Therefore, it makes the system wear and tear, as well as reduces the efficiency of the system.
Secondly, car owners with electronic ignition systems must perform maintenance a lot more often than distributorless ignition systems. With DIS, your car needs to be checked every 100,000 miles, while the service period for the electronic ignition system is 25,000 miles, which is four times longer.
Thirdly, the accuracy of spark timing of the electronic ignition system will reduce over time.
Lastly, the distributor as well as the point gap of the distributor need to be checked regularly.
The cause of issues
You must have noticed by now that all these issues are caused by one single car part: the distributor. And the idea of making a smart ignition system called a distributorless ignition system (DIS) appeared. With this invention, the spark time accuracy is raised with the help of an electronic control unit and ignition module.
Not to mention, with multiple ignition coils, the distribution of the high voltage signal to the spark plugs is straightforward. This helps reduce the wear and tear of the whole system. All of these make the DIS the most reliable and efficient ignition system today.
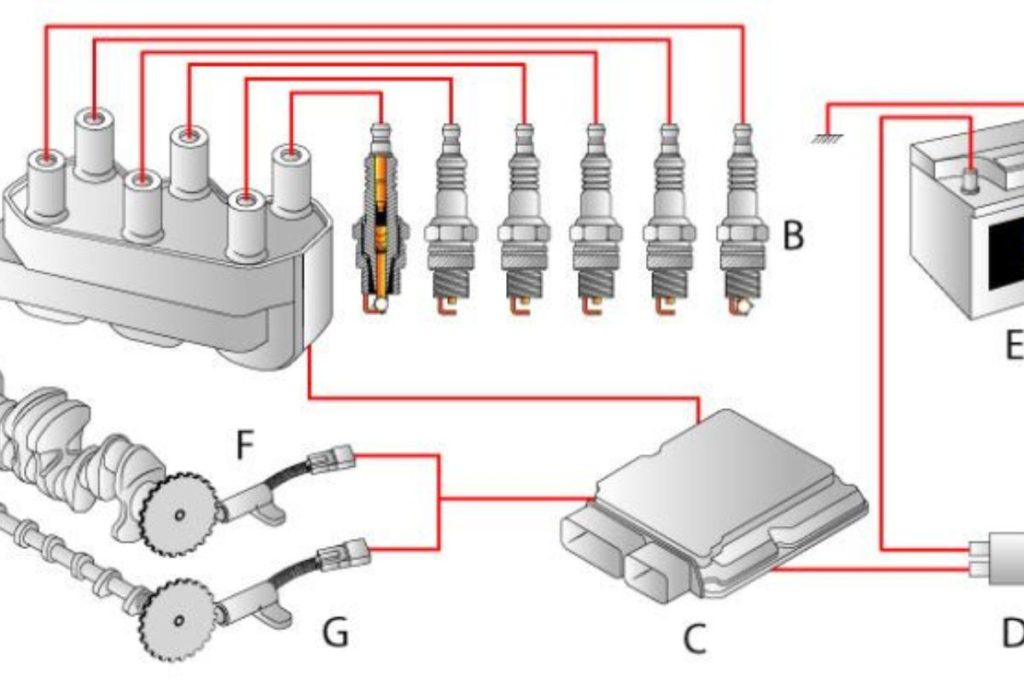
Distributorless Ignition System Main Parts
The DIS shares many similarities in main components with the electronic ignition system. And they are:
Ignition Switch
This is the most basic part of the ignition system that governs the ON and OFF.
Battery
The same with the electronic ignition system, we use the powerhouse to charge the battery.
Magnetic Triggering Devices
Another crucial component is the device controlling the spark plug’s timing. This device senses the crankshaft and camshaft’s location. To be more specific, the crankshaft triggering device is the part mounted on the crankshaft. This part also senses the piston position. Meanwhile, the camshaft triggering device is connected with the camshaft and senses the timing of the valve.
Spark Plug
A spark plug is one of the key components in the distributorless ignition system. The role of the spark plug is to generate a spark inside the cylinder.
Ignition Control Module
This is the programmed instruction for the chipset. If you are wondering about the working function of the primary coil circuit for the ON and OFF buttons, this ICM, or Ignition Control Unit, is the one.
Ignition Coil
Last but not least, these ignition coils together generate high voltage for spark plugs.
How Distributorless Ignition System Works
Now we all know the definition, as well as the main components of distributorless ignition systems. It is time to acknowledge its working function.
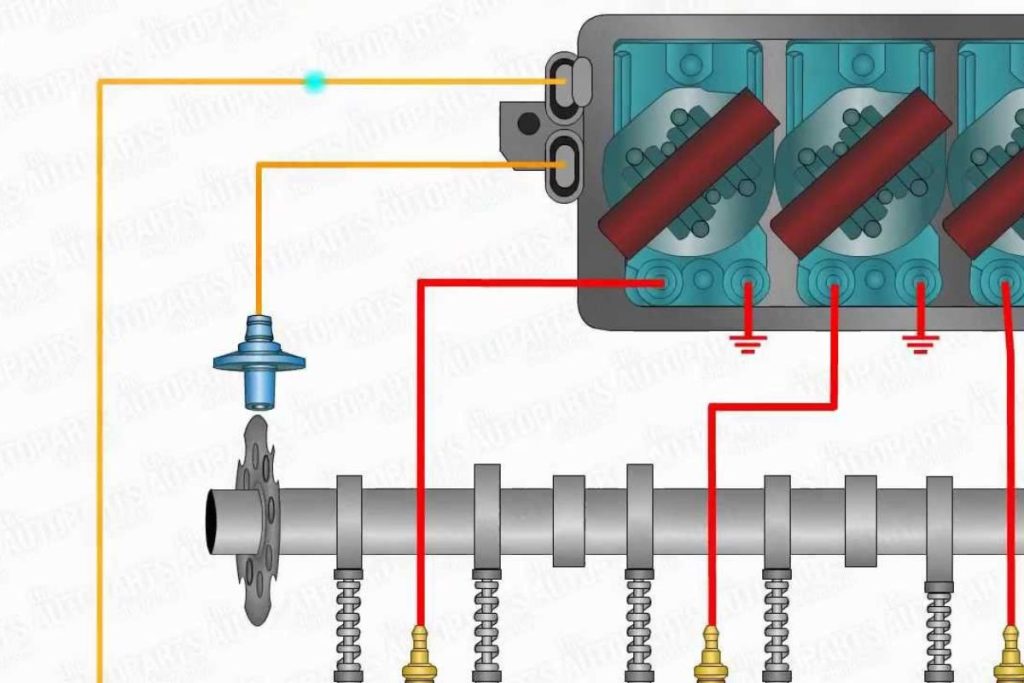
The current
First of all, when we turn on the ignition, the current inside the battery begins to flow. It will run to the ignition switch to the electric control unit of the car, which is connected to the coils and ignition module. This action makes and breaks the circuit.
Create magnetic field
Secondly, we want magnetic fields to make the whole system work. And in order to do that, we need the camshaft and crankshaft. To be more precise, the triggering wheels mounted on these magnetic triggering parts have equally spaced teeth with a gap, along with the position sensors that will generate magnetic fields.
Make and break the signal
Third, when the gaps come right in front of the sensors, there will be fluctuations in the magnetic field. Along with the signals from both sensors, they all come to the ignition module to sense the signal in turn.
This signal makes the current stop flowing in the primary winding of the coils. So what happens when the gaps go away shortly after? The sensor’s signals are sent to the ignition module, followed by turning ON the current to flow in the winding of the coils.
Raise the voltage
Fourth, this whole process of making and breaking the signals eventually generates a magnetic field and induces EMF in the secondary winding of coils. And it will raise the voltage to nearly 70000 volts. And the spark plugs receive this voltage. After that, the generation of sparks will happen.
Last of all, the electronic control unit controls the spark plug’s timing. The working mechanism of this unit is by continuously processing the data from the ignition control module.
Why DIS Is Better?
The Distributorless Ignition System (DIS) is a major upgrade over the old-style distributor for a few key reasons. The biggest one is that DIS has no moving parts. The old distributor used a spinning rotor and a cap, which would wear out over time and needed regular replacement. By getting rid of these mechanical parts, DIS is much more reliable and requires almost no maintenance.
This new system also gives a car’s computer a lot more control. Instead of a mechanical system, the computer uses sensors to know exactly when to fire each spark plug. This precise timing means the engine runs more efficiently, giving you better gas mileage and more power.
The coils in a DIS can also create a stronger spark, which helps the engine run cleaner and start more easily, especially in cold weather. In short, the DIS is better because it’s more reliable, needs less work, and gives the engine a better, more powerful spark.
We hope that this knowledge about the distributorless ignition system will be useful for you. Follow our car maintenance for more information.



