The wheels’ size, offset and backspacing is critical for its installation and replacement in the vehicle. However, it is quite difficult for people to understand, and for service professionals to explain its concept. However, if it is not handled with skillful knowledge then, it can cause a serious risk of a blowout to the drivers.
Therefore, here the wheel offset and wheel backspacing explained for the safety of your vehicle and more importantly, yours.
SEE MORE:
Contents
Guide to Wheel Offset
Firstly, it is vital to understand that apart from the safe run on roads, this characteristic offers custom-looking wheels to the user. However, if the offset of the wheel is not in accordance with the car then, it may cause several issues. For instance, wheels not rotating freely as per the instruction and may rub with the fender or the brakes. Therefore, for the proper offset of the wheel, it is measured from the mounting surface to the rim’s true centerline of the wheel.
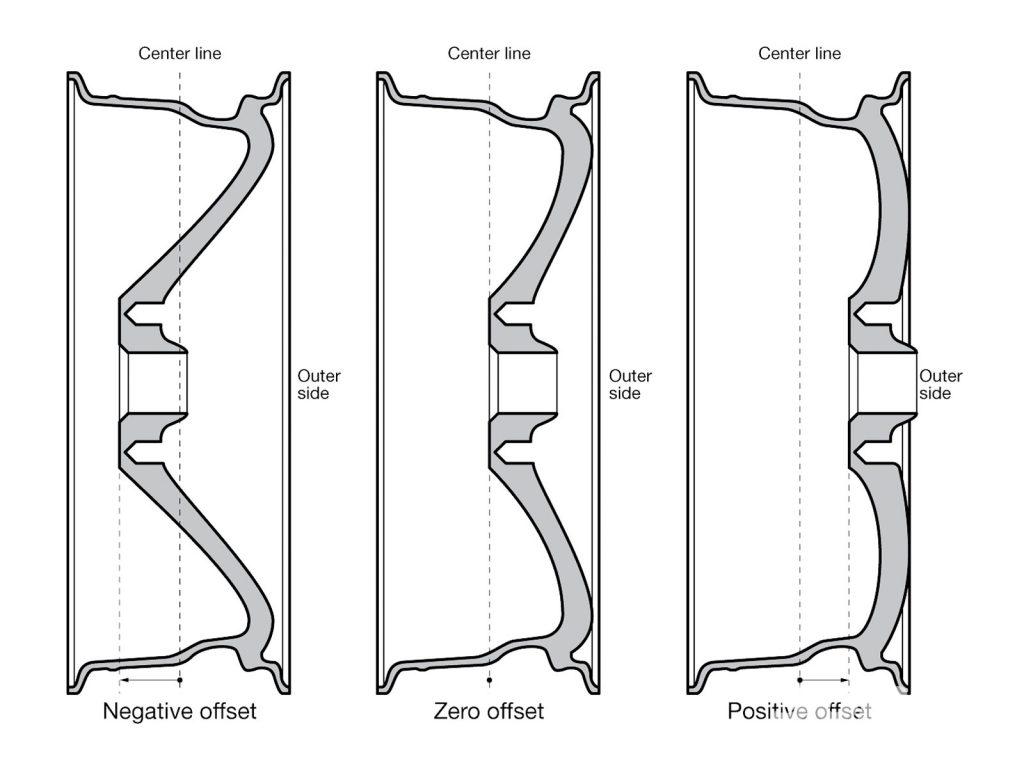
Usually, the offset of the wheel is measured in the standard unit called millimeters and on its basis is classified into three types:
1. Negative Offset
This kind of offset means, the hub-monitoring surface is closer to the inside edge of the wheel and the wheel sticks more outwards than inwards. This kind of offset benefits the design process by allowing sharp angles, deep spokes and incredible layering.
2. Zero Offset
In this case, the hub-mounting surface is even with the centerline of the wheel.
3. Positive Offset
When the hub-mounting surface is closer to the outside edge of the wheel, it is referred as the positive offset. In this case, the wheel actually wraps around the hub and brake more deeply. It is commonly found in wheel drive and newer rear drive cars.
Guide to Wheel Backspacing
Backspace is referred as the distance from the back edge of the wheel to its mounting surface. “Back” here means the brake side of the wheel. It is normally measured in inches.
However, it is considered as the traditional system of measuring the depth of mounting pad in the wheel. Accurate backspacing allows enough space for the suspension, brake, and steering system to operate without the interference from the wheel.
This, above guide where we have wheel offset and wheel backspacing explained will help you further understand more of it, by learning about its measurement now.
How to Measure Wheel Offset
For measuring the wheel offset, following three measurements are essential,
Wheel Backspace
It’s Width and,
Wheel Centerline (Outboard Flange to Inboard Flange Measurement)
Then, subtract the measurement of centerline from the wheel backspace, in order to know the offset. If the backspace is less than the centerline, it is negative offset.And, if it is greater than the centerline, it is called positive offset.
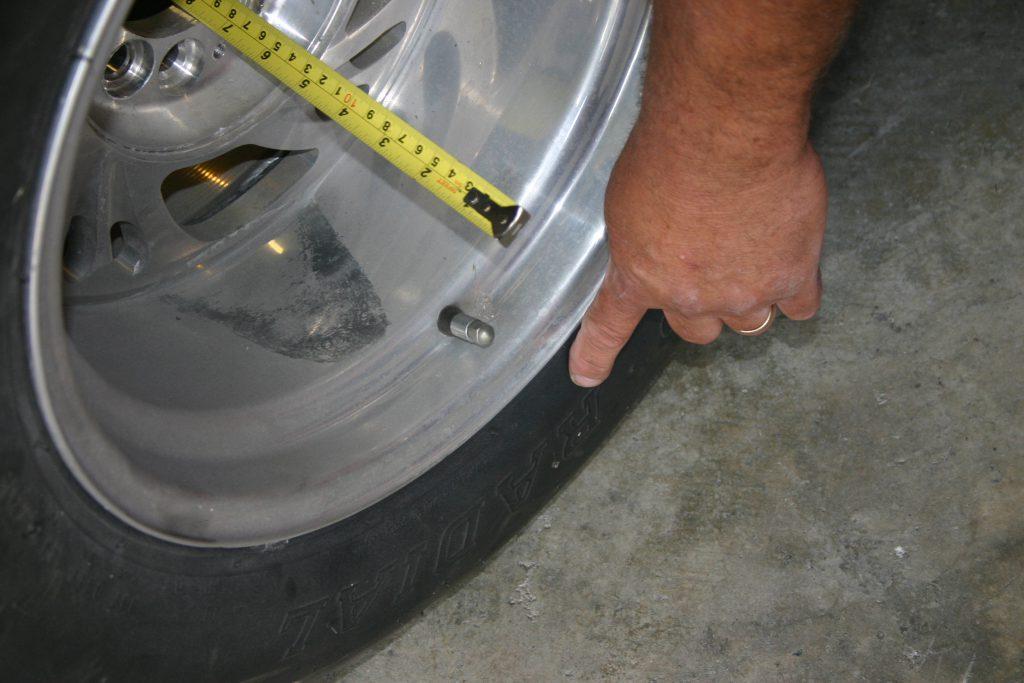
How to Measure Wheel Backspace
In order to measure the backspace, keep the wheel on the floor so that its backside is facing upward. Now, with the measuring tape, calculate the distance from the hub-mounting pad to the joint where straight edge contacts the inboard flange. This measurement is the backspace.

So, the wheel offset and wheel backspacing explained above would be very helpful to the technicians. In addition, they can now easily guide people regarding the same and give certain maintenance tips for it.



