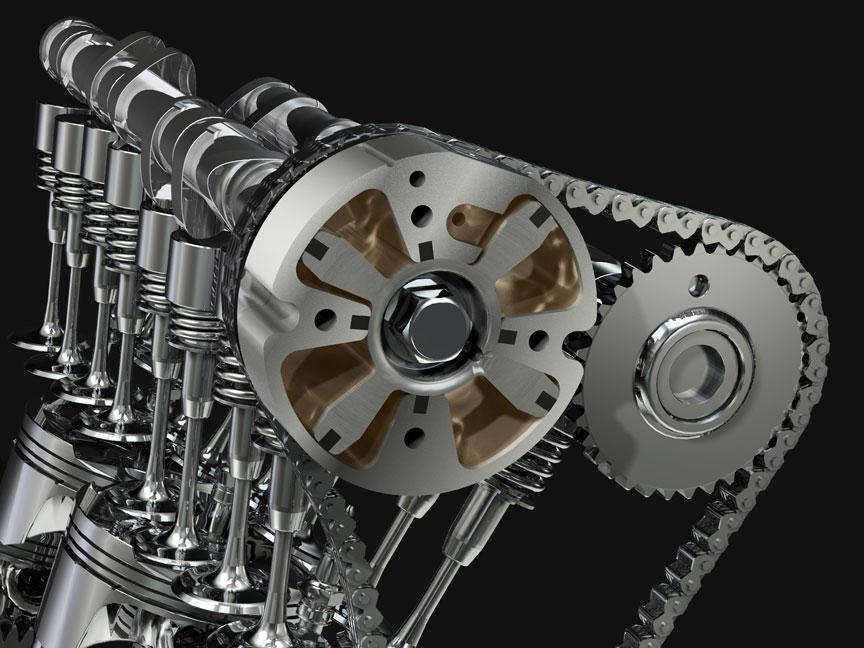
Modern cars have all types of sensors and gadgets, and they also have a central computer system for smooth operation.
There are so many things going on under the hood, and you don’t even need to know the functions of half of these parts.
However, if you are a car enthusiast, you should know about some important components, and learning how variable valve timing works is one of them!
Contents
- Definition of Variable Valve Timing
- Important Parts of Variable Valve Timing
- How Variable Valve Timing Works?
- FAQs on Variable Valve Timing
- Can Variable Valve Timing affect fuel efficiency?
- How does VVT influence engine noise and vibration?
- Does VVT complexity affect the reliability of the engine?
- Can I retrofit Variable Valve Timing to an older engine?
- How does VVT interact with turbocharged engines?
- Is there a significant difference between VVT systems among manufacturers?
Definition of Variable Valve Timing
The variable valve timing systems are seen in the internal combustion chamber of an engine. It does the job of changing the timing of a valve’s opening and closing and works together with the valve lift system.
This component is important because its proper use can enhance engine performance, increase fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions.
The two-stroke engines don’t have a VVT, but they use power valve systems to produce the same type of performance.
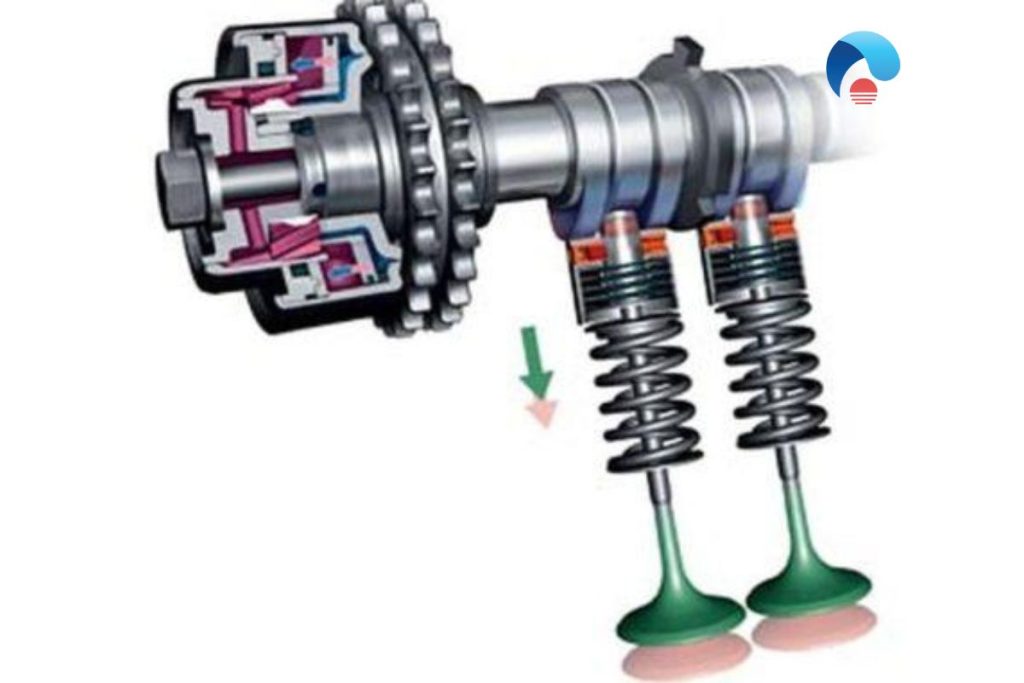
Important Parts of Variable Valve Timing
The entire VVT system and its components depend on the engine oil circulation. If there’s any problem with the oil flow, all the parts can fail permanently.
The two most important parts of this system are:
Solenoids
Each camshaft has a solenoid that works on the oil pressure to the camshaft. It can change the pressure based on the engine load and speed.
It also helps to induce the right performance of the engine by enhancing or blocking the cam position.
This component can fail because of two reasons – irregular oil changing in the filters and engine, and low level of oil in the engine.
See More: How to Diagnose an Engine that Doesn’t Start
Sprockets
Also known as cam phaser, this device does the job of maximizing torque curves and enhancing engine horsepower.
It ensures that your car is getting the best performance from the engine while releasing less carbon footprint.
How Variable Valve Timing Works?
There are several valves to be found inside the combustion chamber on an engine. These are responsible for controlling the gas flow entering and exiting the combustion cylinder.
Without a VVT, the timing of all the valves will be the same for every engine condition and speed. It hampers the performance because the timing should be adjusted to these factors.
A variable valve timing allows the changing of timing based on speed and engine condition. There are two major types of VVT systems. Let’s have a look:
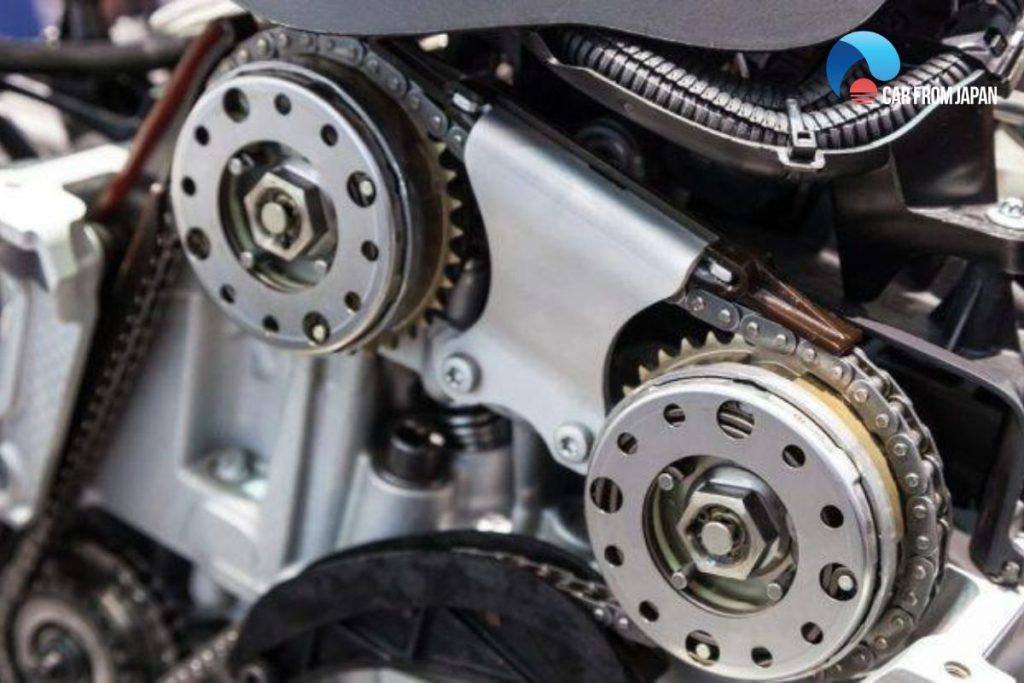

Cam Phasing
It rotates the camshaft over a range of 60 degrees to boost or check valve lift events. For example, a valve can open and close at 5 and 185 crankshaft degrees, respectively, before and after top dead center.
If the valve timing restrains the lift events by 10 degrees, the valve will open and close at 10 degrees later, respectively.
It will help the engine to produce better power at high RPM while advancing the timing will enhance the power at low RPM.
Cam Changing
It changes the angle of the camshaft phase to the crankshaft along with the shape of the camshaft lobes.
These changes affect the opening of the valve and the duration it will stay open. Such alteration to the timing of the valves’ operation helps a vehicle to achieve its maximum efficiency.
FAQs on Variable Valve Timing
Can Variable Valve Timing affect fuel efficiency?
VVT significantly improves fuel efficiency by optimizing the opening and closing times of the intake and exhaust valves according to engine speed and load.
This precision allows the engine to breathe more efficiently at different RPMs, reducing fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining optimal performance.
How does VVT influence engine noise and vibration?
VVT systems can actually help reduce engine noise and vibration.
By optimizing valve operation, the engine runs smoother at various speeds, leading to reduced noise and less perceptible vibration.
This contributes to a more comfortable driving experience, especially at high speeds or under heavy load.
Does VVT complexity affect the reliability of the engine?
While VVT systems add complexity to the engine, most modern engines are designed and built to high standards of durability and reliability.
Can I retrofit Variable Valve Timing to an older engine?
Retrofitting VVT to an engine not originally equipped with it would be highly complex, costly, and, in most cases, impractical.
VVT systems are integrated into the engine design and controlled by the engine management system, requiring significant modifications to both hardware and software.
How does VVT interact with turbocharged engines?
In turbocharged engines, VVT enhances performance and efficiency by optimizing valve timing to manage the flow of exhaust gasses more effectively, improving turbocharger response.
This results in better low-end torque and more consistent power delivery across the engine’s rev range.
Is there a significant difference between VVT systems among manufacturers?
While the basic principle of VVT is consistent across the automotive industry, manufacturers may implement different mechanisms and control strategies.
Some use hydraulic actuators, while others might use electric motors to adjust valve timing.
The specific design and implementation can affect the system’s responsiveness, efficiency, and overall impact on engine performance.
Check out this video from Engineering Explained to learn more about variable valve lift vs variable valve timing!
Now you know how variable valve timing works and some common questions asked related to this component.
For more insightful Car maintenance tips, follow Car From Japan today!