Some drivers assume that a catalytic converter can last the full life of your car when the car is maintained properly. But this opinion is really true? Let’s find the secrets of the lifespan of the catalytic converter to have an answer to the question How long do catalytic converters last?
Contents
What Is A Catalytic Converter?
Emission from your car is considered an enemy to the environment. To reduce these harmful substances, the automaker created a catalytic converter that converts harmful emissions into other forms of waste that have less impact on the environment. Catalytic converters are commonly used on internal combustion engines that use gasoline or diesel fuel. When your vehicle is in operation, the fuel combustion process of the engine will emit major wastes such as CO2, H2O, and N2 (78%). These substances are almost harmless to the environment if the process of material combustion takes place thoroughly.
However, in fact, no matter how good the engine is, the combustion process can still produce a small amount of other harmful compounds such as carbon oxide (CO), nitrous oxide (NO, NO2 gas), and hydrocarbon (HC). So what does a catalytic converter do in your car? The main task of the converter at this time is to turn toxic substances into less harmful compounds (CO2) or possibly into substances that are not harmful to the environment such as N2, and H2O before emitting them into the environment. To make this process, the converter needs to consume a layer of precious metal to catalyze the reactions more easily and quickly. Catalytic converters can convert about 90% of environmentally harmful compounds into less harmful ones. Some high-end car manufacturers today equip special filters, which can significantly increase the working efficiency of the car converter by up to 99%, helping to better protect the environment.
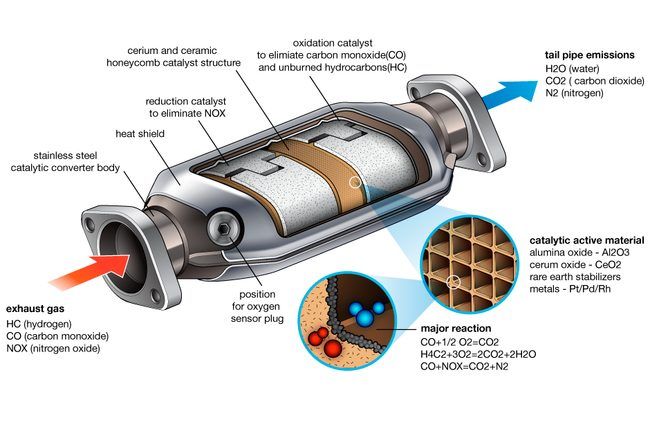
Do Catalytic Converters Go Bad?
As we mentioned at the opening, many people think that the catalytic converter can last for a long time if well-maintained so does a car converter go bad or wear out? Catalytic converters can go bad over time due to a variety of reasons. One common cause of failure is contamination or damage to the internal components, such as the ceramic substrate or the catalyst coating. This can occur if the converter is exposed to high levels of unburned fuel, oil, or coolant, which can lead to overheating or clogging of the converter.
Another factor that can contribute to the failure of a catalytic converter is physical damage, such as impact from road debris or corrosion from exposure to salt or other chemicals. In addition, if the engine is running poorly or experiencing misfires, it can cause excessive stress on the converter, leading to early failure. It’s important to note that catalytic converters are designed to last for many years, and failure is relatively rare. However, if you notice symptoms such as a decrease in engine performance, increased exhaust emissions, or rattling noise coming from the converter, it may be a sign that the converter needs to be replaced. It’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic for diagnosis and repair.
How Long Do Catalytic Converters Last in Your Car?
The lifespan of a catalytic converter can vary depending on a number of factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, the quality of the converter itself, and the conditions under which the vehicle is driven. In general, a catalytic converter can last anywhere from 50,000 to 150,000 miles or more. And these miles will be equivalent to around 10 years. However, there are a number of factors that can cause a catalytic converter to fail prematurely, including:
- Fuel contamination: If your engine is burning oil or running too rich, unburned fuel can contaminate the catalyst and cause it to fail.
- Physical damage: The catalytic converter can be damaged by road debris or impact with speed bumps or other obstacles.
- Overheating: Extreme temperatures can cause the catalytic converter to overheat and melt.
- Rust and corrosion: Exposure to moisture and salt can cause the catalytic converter to rust and corrode over time.
If you suspect that your catalytic converter is failing, you should have it inspected by a mechanic as soon as possible. A failing catalytic converter can cause a variety of problems, including reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and even damage to other parts of the engine.
What Happens When Catalytic Converters Go Bad?

The catalytic converter is located on the vehicle’s exhaust system and is essential to controlling the vehicle’s emissions. It basically ignites the exhaust gases and converts them into steam and oxygen. So when this part is going bad, you can easily identify through abnormal signs from the engine and fuel consumption:
1. Poor performance
One of the first symptoms often associated with a faulty or damaged catalytic converter is reduced engine efficiency. The catalytic converter is integrated into the vehicle’s exhaust system, and as such, can affect the engine’s performance if it develops any problems. A clogged converter will restrict exhaust air flow, while a cracked converter will leak harmful gases. Either fault can negatively affect engine performance and reduce power and acceleration as well as fuel economy.
2. Strange noise or smell
If you notice the popping noise from under the vehicle is another symptom of a damaged catalytic converter. If a catalytic converter becomes old or has internal faults from excessively rich fuel mixtures, the honeycomb grids coated with the catalyst on the inside of the converter can rupture, causing a popping sound. The noise may be more pronounced when starting the vehicle and will worsen over time.
During engine combustion, the sulfur-containing fuel becomes hydrogen sulfide. A properly functioning catalytic converter will convert hydrogen sulfide to odorless sulfur dioxide. When damaged, you may notice a sulfurous odor emanating from the exhaust. Unburnt fuel left in the exhaust by a damaged catalytic converter will produce an odor, and may even cause black exhaust fumes.
3. The check engine light is on
A damaged catalytic converter can also cause the check engine light to come on. Oxygen sensors and air-fuel ratio sensors in modern vehicles monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter by monitoring the fuel level in the exhaust. If the computer detects that the catalytic converter is not working correctly or not catalyzing the emissions properly, it will turn on the Check Engine light to alert the driver of the problem. A variety of other problems can trigger the Check Engine Light, so it’s a good idea to scan your vehicle for trouble codes to be sure of the problem.
Watch the video to know when your car need a new catalytic converter:



