DC Fast Charging: Everything You Need To Know
Although on average, the batteries on electric vehicles (EVs) vehicles take about 8 hours to charge from empty to full, the number can range widely, being anywhere from 30 minutes to 12 hours. This depends on the charging speed that your EV allows. While there’s the option for charging with alternating current or AC charging, charging with direct current or DC charging allows for a much shorter but efficient charging time. Read on to learn the difference between the two types of charging, how DC fast charging works, and what types of plugs and cables you’d need for DC charging.
AC Charging vs DC Charging: A Comparison
Before we start, it’s essential that you understand the two kinds of electrical power or ‘fuels’ that electric cars consume, since they allow for two types of charging with different charging speed: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). While the power coming from the grid is always AC power, batteries like the one in your smartphone or electric vehicle only store power as DC.
This means that your EV as well as most electronic devices have a converter built into the plug for converting AC power from the grid to DC power, which the batteries can store. With EV charging, the difference between AC charging and DC charging is whether the AC power gets converted inside the car or outside.
AC Charging
AC charging is the standard and still currently most common charging method for electric vehicles. All electric vehicles have a built-in converter inside, which is called the onboard charger, to convert power from AC to DC and then feed it into the car’s battery. The conversion happens inside the car with AC charging
DC Charging – Fast Charging
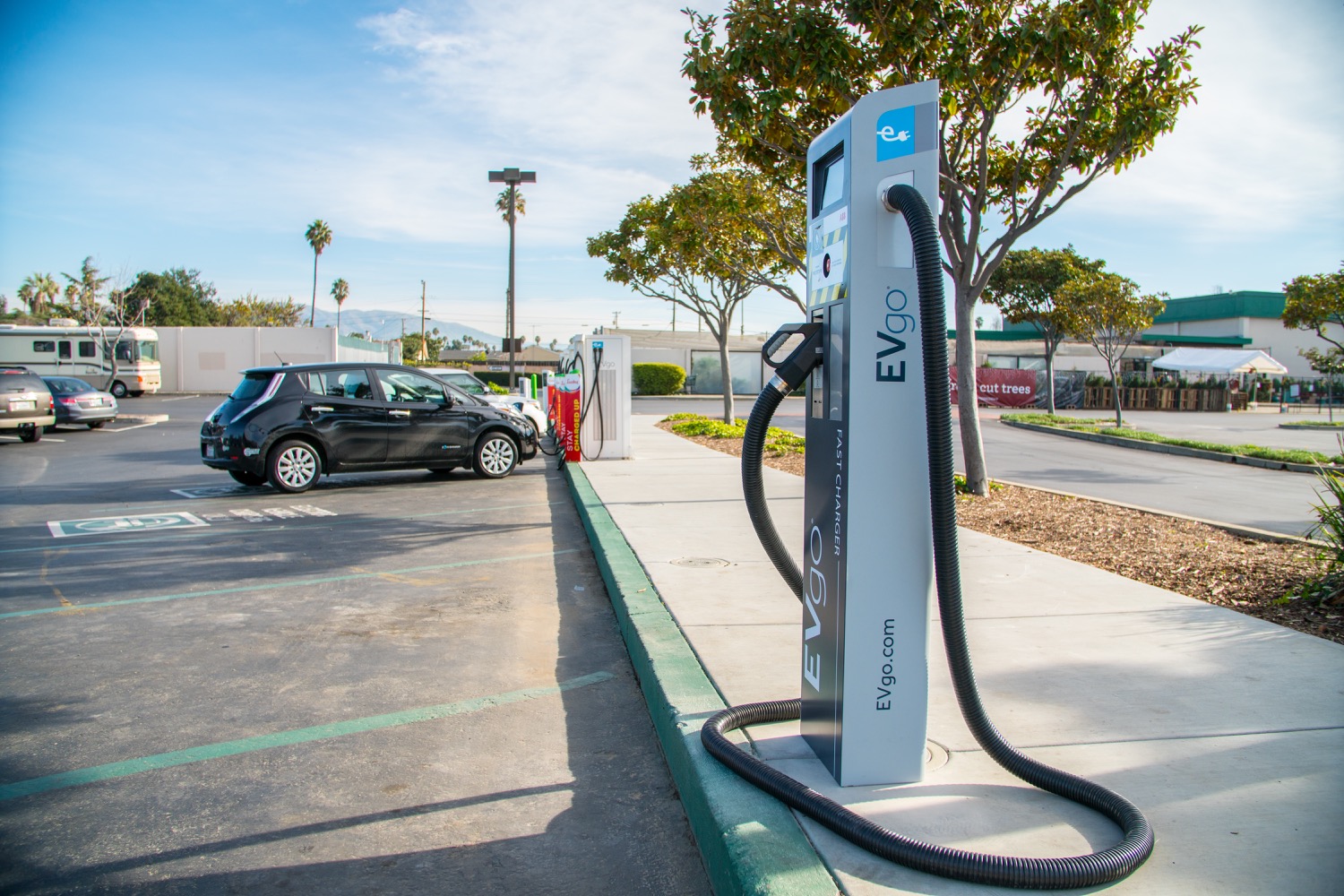

Unlike AC charging, the conversion from the grid’s AC power to DC power happens inside the DC charger, thanks to the built-in converter inside the charger itself. This means there is no need for the car’s onboard converter, since the DC charger can convert AC power to DC and directly feed DC power to the car’s battery. DC chargers available at public charging stations make for an exciting breakthrough with much faster charging speed.
In any case, one thing is absolutely essential: you need the right plug. That is, the cable that connects your EV with the public charging station or any electric socket you intend to use has to have the right plug on both ends. In other words, two things have to match: the outlet of your green vehicle and the outlet of the charging station.
In general, there are two major types of standard plugs at public charging stations for alternating current (AC) which allow a charging speed of up to 43 kW, and two types of standard plugs for direct current (DC) which allow much fast charging of up to 350 kW. The other special DC plug is the one developed by Tesla and offered exclusively to Tesla EVs, which will be introduced at the end.
READ MORE
What You Need for DC Fast Charging
DC chargers use the built-in converter to directly feed direct current (DC) rather than alternating current (AC) to an EV’s batteries. They are bigger and allow for a faster charging experience. This type of charger usually takes about 20 minutes to charge your battery to 50 percent and takes about 75 minutes to restore it to a full charge.
For DC fast charging, you can use three different types of charging plugs:
CHAdeMO
This quick charging system was developed in Japan, and allows for charging capacities up to 100 kW at the appropriate public charging stations. Since it allows for very high charging capacities as well as bidirectional charging, Asian automakers have been manufacturing electric vehicles that are compatible with a CHAdeMO plug. The brands that offer CHAdeMO-compatible electric cars include Nissan, Toyota, Honda, Kia, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Subaru, Peugeot, Tesla (with adaptor), BD Otomotive, and Citroën.
Combined Charging System
The Combined Charging System, or Combination Plugs (CCS) is the successor of the type 2 plug, with two additional power contacts for enhanced charging speed. It supports both AC and DC charging, with a maximum charging power level of 350 kW. In practice, the realistic number is usually around 170 kW. The automakers that offer EVs using CCS plug include Ford, BMW, Volkswagen, Chevrolet, Mercedes, and Volvo.
Tesla Supercharger
Tesla developed its own network of fast-charging Supercharger stations exclusively for Tesla owners. If you own a Model S, you only need less than 30 minutes to recharge to 80%. Tesla also sells adapters so that you can charge your Tesla EV at CHAdeMO or CCS charging stations.
Tesla Superchargers stations are conveniently installed along popular routes throughout the world, often at high-traffic public places such as fueling stations and large shopping malls, so you can spend time elsewhere shopping or running errands while your vehicle charges. As of early 2021, there are currently over 23,277 Superchargers in over 2,564 stations across North America, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia, or an average of 9 chargers per station.